Jeff Bezos once said, “There are two kinds of companies, those that work to try to charge more and those that work to charge less. We will be the second.” And it won’t be wrong to say that Amazon is constantly trying to achieve lower prices for its enormous user base.
Amazon has become a one-stop destination for everyone’s shopping needs and is correctly called ‘the everything store’.
Today, the company has a market capitalisation of $117 billion. With such a complex ecosystem comprising several entities and millions of customers, it is crucial to understand every aspect of this ecommerce giant’s business model.
Dive right in to know all about Amazon’s business model, operating model, and revenue sources.
Amazon Business Model
Amazon has come a long way from being a simple, one-sided ecommerce company to developing its own massive ecosystem. Today Amazon has incorporated various units within its business model, including a one-sided platform, two-sided marketplace, web services, kindle marketplace, an app store, prime video, game studio, and even retail stores called Amazon Go. All these diverse ventures add to the revenue stream of Amazon, making it one of the biggest companies in the world.
Although Amazon deals in numerous products and has set foot in multiple industries, its core business model is based on an ecommerce market platform. Thus to completely understand the massive business model of this tech giant, it is crucial first to take a look at the Amazon marketplace.
What Is Amazon Marketplace?
Amazon first started as a digital bookstore when only 0.447% of the total world population had access to the internet. Today it has evolved into the world’s largest retail marketplace platform and is popularly called ‘the everything store.’
The Amazon marketplace is an online two-sided ecommerce platform where third-party sellers and Amazon sells products from various categories, including electronics, gaming products, apparel, home decor, B2B business products, garden products, etc. The marketplace provides a platform for buyers and third-party sellers to interact and trade.
Amazon marketplace also includes the Kindle store, which allows readers to browse and download various e-books, newspapers, magazines, etc. Thus, the marketplace provides a platform to publishers and readers where they can trade and interact.
Who Are Amazon’s Customers And What Value Does It Provide?
Amazon’s consumers are the people who use the marketplace for their shopping needs. The platform provides multiple options to the consumers at the lowest prices with fast deliveries and an overall enhanced shopping experience.
Amazon is a customer-centric company and provides immense value to its customers through its easy-to-use and easy-to-browse interface, review systems, recommendations, and gift certificates. Moreover, the platform has greatly reduced the shopping time as now customers complete around 28% of their purchases in three minutes or less. All these features combined contribute to customer value creation which gives them more incentive to use the platform. According to Amazon’s annual report, the total customer value creation in 2020 itself was $164 billion!
Amazon’s Operating Model
Amazon operates on the business model of a two-sided marketplace. It provides a platform for the buyers and sellers to easily interact and trade with each other without much hassle or difficulties. The company has designed a vast operating model to fulfill the needs and demands of each consumer. It manages the production, packaging, shipping, and delivery of a large number of products to provide everything to customers at the lowest possible price.
Key Resources
Amazon uses various resources to keep its business up and running.
- One of the major resources is its warehouses and fulfilment centres used for packaging, shipment, and delivery of products.
- Amazon’s technological infrastructure, including the website, the app, and the developers, are extremely important for the platform’s functioning.
- Other resources include the company’s executives in various departments, including customer relationship management, marketing, content development, etc.
Key Partners
Amazon’s key partners are the sellers or the merchants who use the marketplace to reach buyers and sell their products. Amazon provides a platform to such third-party sellers to easily interact with an established base of buyers and trade with them. It has partnered with many third-party sellers who offer a wide variety of products and hence provide multiple options to the buyers.
Although sellers are the partners, Amazon treats them as its customers as they can either sell on Amazon or some other marketplace.
Key Channels
Amazon delivers its services to the customers through three main channels including:
- The Amazon website,
- The application, which is available on PlayStore as well as App Store and,
- The physical stores called Amazon Go where the company has harnessed technology to provide an easy and speedy shopping experience.
Customer Relationships: Reviews And Customer Service
One of the main goals of Amazon’s business model is to constantly enhance customer experience on the marketplace and build strong customer relationships. The company has always been customer-centric and has successfully mastered customer relationship management by offering convenience, low prices, multiple options and an overall enhanced shopping experience. Some of the strategies used by Amazon for customer relationship management are:
- Easy to use interface: The platform’s user interface is extremely easy to use and understand. The high-quality images, accurate descriptions, easy checkout process and organised categories of products greatly enhance the shopping experience and hence induce customers to spend more time on the platform.
- Recommendations: The product recommendations and product bundling based on the past buying behaviour of customers are perfect for boosting sales while simultaneously offering a convenient shopping experience.
- Customer support: Amazon tries to limit the need for customer support and makes self-help easy for customers if they get stuck anywhere. However, the company understands the importance of an efficient customer support system where the consumers have 24/7 support available for any of their queries or problems.
- Review system: Amazon also has an online review system where customers can share their experiences and opinions about a certain product and even upload pictures. The social validation system connects the buyer community and also ensures good quality standards on the marketplace.
Network Effect
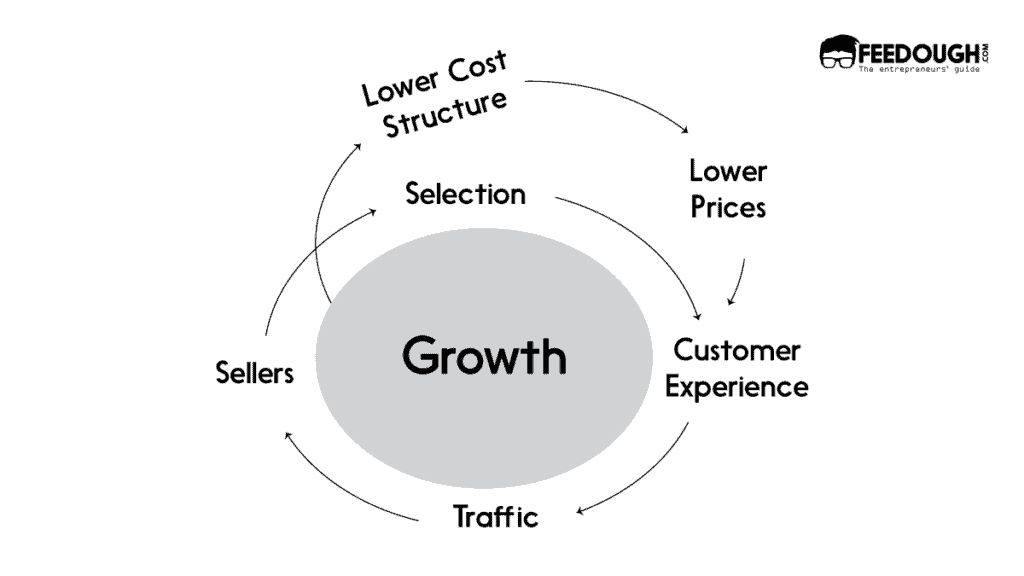
In 2001, Jeff Bezos, CEO and founder of Amazon, drew up Amazon’s famous virtual cycle that aptly describes the company’s business model.
Amazon’s key objective has always been selling products at the lowest prices. That is why even though the company has the opportunity to translate its lower cost structure into profits and return some profits to shareholders, it passes them on to the customers through network effects.
The network effects create a loop where the low prices of products on Amazon enhance customer experience, driving more traffic to the platform. The increase in traffic and number of customers induces more third-party sellers to join the network, increasing the options available to the customers. This, in turn, further enhances the customer experience by providing various categories of products at low prices.
Moreover, Amazon uses the revenue generated from increased sales to improve its cost structure further. A big portion of the revenue goes to improve fulfilment and delivery networks which further lowers the cost structure. Amazon has used network effects and marketing strategies since the very beginning, which has helped the company to expand and take over various industries successfully.
Amazon Fulfilment Options: The Supply Chain
Inventory management is a key task for Amazon as the company deals in such a wide variety of products. Amazon provides various fulfilment options to the merchants, including:
- Fulfilment By Amazon (FBA) where Amazon stores, packs and ships the product through its fulfilment centres
- Easy Ship where the merchant stores and packs the product but Amazon delivers it.
- Fulfillment By Merchant (FBM) where the merchant handles storage, packaging and delivery of the product.
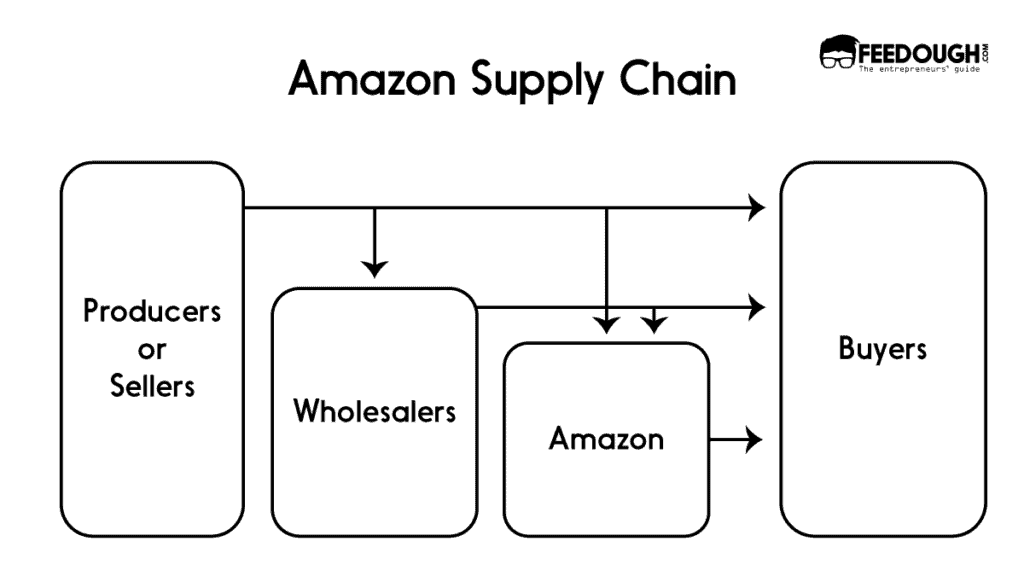
Therefore, Amazon stores most of the products placed on the marketplace and hence has to manage a large amount of inventory. So to satisfy customers with speedy delivery, the company has managed to create an efficient inventory management system and order picking process. Each product in the Amazon distribution network goes through 5 centres:
- Crossdock centres where packages from vendors are stored until more stock is required
- Fulfilment centres where the products are stored and packed for delivery.
- Sortation centres where packages are sorted and routed by zip code before sending them to delivery stations.
- Delivery stations where deliveries are handled by USPS, FedEx or UPS.
- Amazon Prime Now Hubs where Amazon manages the products which have to be delivered within 2 hours of purchase.
How Does Amazon Make Money?
Amazon works on a complex business model with various value propositions and different customers. But its main source of revenue is the marketplace and ecommerce stores which form the foundation for its other businesses. For example, in 2019, the company had net sales of $280 billion and a net profit of $11 billion, and around 50% of sales were from ecommerce stores.
Revenue Sources
The Amazon marketplace has multiple revenue sources such as:
- Sales: Amazon works as an ecommerce platform and sells its products on the platform. A considerable percentage of Amazon’s revenue comes from the sales of these products. The company competes with other third-party sellers and brands to attract customers on the marketplace and promotes its own brand.
- Listing fee: Amazon charges a listing fee from third-party sellers to list their products on the platform. The fee starts at 2% of the product price and varies for various categories of products.
- Commission or Closing fee: Amazon charges a commission from the merchants every time a product is sold through the platform. The commission depends on the price of the said product and the fulfilment channel used by the merchants.
- Prime subscriptions: Amazon also offers prime subscriptions to the customer for an enhanced shopping experience on the platform. The prime members get access to unlimited free, fast deliveries, prime video where they can stream the latest movies and tv-shows, prime music where they can enjoy ad-free music streaming along with unlimited offline downloads, free in-game content on popular mobile games, unlimited 5% reward points, prime reading, and exclusive access to top deals and coupons. The membership costs $119 per year and $12.99 per month.
- FBA (Fulfilled by Amazon): Amazon offers various fulfilment options to merchants. They can either go for FBA, where Amazon stores, packs, and delivers the product to the customer, or they can go for easy shipment where the merchant stores and packs the product while Amazon delivers it. The company charges a different fee based on the option chosen by the merchant.
- Kindle direct publishing: Amazon offers publishing services to independent authors as well as publishers. The company publishes the book, makes it available on the kindle store, and provides the author 70% royalty.
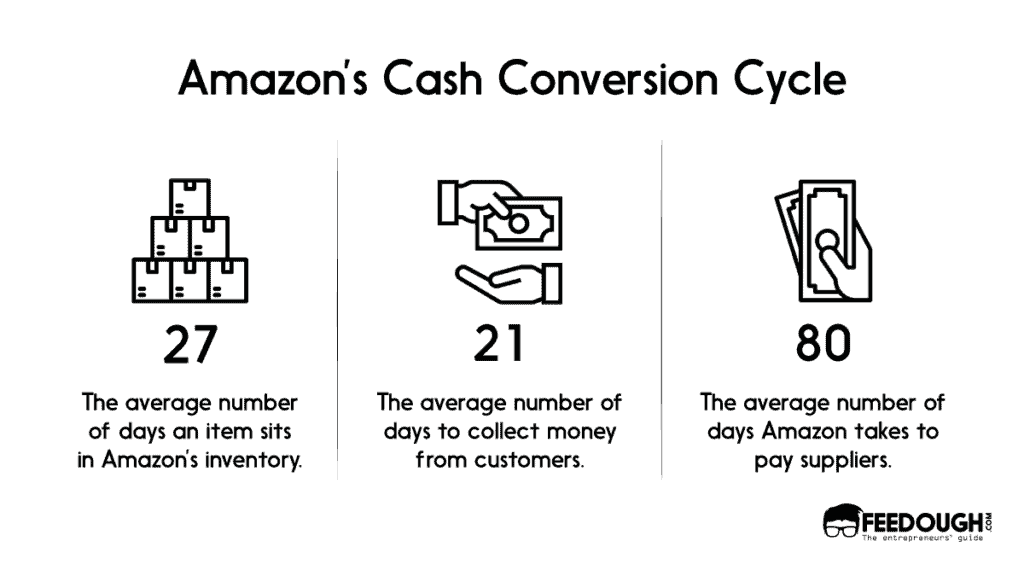
Cash Conversion Cycle
Amazon’s cash conversion cycle is one of the most important strategies of its business model. The company generates short-term liquidity by receiving payments from the customers before paying for the product to the suppliers. This allows Amazon to invest in its growth using the suppliers’ balance rather than being tied up in the inventory loop.
Using this mechanism, Amazon has successfully dominated various industries and diversified its portfolio from being an online bookstore to ‘the everything store’.
What Makes Amazon’s Business Model Unique: The Pricing Strategies
Amazon is known for its low and competitive prices across diverse categories of products. However, the Amazon business model depends on offering the lowest prices to the customers and offering prices that reflect market changes and keep up with the competition. The company achieves this using artificial intelligence, machine learning and around 1 billion gigabytes of data pertaining to its 1.5 billion products and about 200 million users.
Here are some pricing strategies used by the e-commerce giant to keep its prices up to date:
- Dynamic pricing: Amazon changes the prices of various products on the marketplace about 2.5 million times a day. Thus, an average product listed on Amazon would change price every 10 minutes! The dynamic pricing allows the company to keep its prices competitive and has even helped Amazon boost profits by 25% on an average. The real-time pricing considers data from various sources like customer activity, the available inventory of a product, order history, preferences set for a product, expected margin on the product, and more.
- Psychological pricing: Another strategy used by Amazon to keep its prices competitive and to attract more customers is psychological pricing or price perception strategy. An average customer often finds that prices on Amazon are the lowest among all its competitors. This is because of Amazon’s pricing algorithms. The company provides huge discounts on best-selling and popular products but raises the prices on uncommon products. Now, whenever a customer searches for the most common products on Amazon, they will find the most affordable prices which will further induce them to assume that the platform has lowest prices overall.
- Competition monitoring and repricing: Every retailer on Amazon constantly keeps a tab on the prices offered by its competitors and considers repricing its own products to attract more customers on the platform and achieve the ‘buy box’ position. Amazon uses its algorithms to keep track of the changing prices and tanks the products offered by various retailers accordingly.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about Amazon Business Model in the comment section.
An enthusiastic human being with determination and zeal to explore new ventures. Tanya is an entrepreneurial spirit searching for changes and learning to exploit them as opportunities and impacting people for good.