You ask your AI assistant a complex question. It gives you an answer instantly. Confident. Direct. But also… wrong.
The problem? Most AI models think in straight lines. They pick one path and run with it. No second-guessing. No exploring alternatives. Just A to B, even when B leads nowhere useful.
That’s exactly what Tree of Thought prompting fixes. Instead of forcing your model down a single reasoning path, you let it branch out.
What Is Tree of Thought Prompting?
Tree of Thought (ToT) prompting is a framework that lets language models explore multiple reasoning paths at the same time.
Instead of generating one answer sequentially, the model creates different solution branches. It then evaluates each branch and picks the strongest one.
Think about how you solve a complex problem. You don’t just commit to the first idea that pops up. You consider different approaches. You test them mentally. You abandon paths that don’t work and double down on promising ones. That’s exactly what ToT does for AI.
The framework mimics how humans naturally solve problems by generating thoughts as intermediate steps. Each thought becomes a node in a decision tree. The model can look ahead to see which thoughts lead somewhere useful. It can backtrack when it hits dead ends. This multi-path exploration means better decisions on tasks requiring planning, strategy, or creative problem-solving.
How Tree of Thought Prompting Works
Think of ToT as building a map while you navigate. When you face a complex problem, the AI doesn’t commit to one path right away. Instead, it breaks the problem into a decision tree where each branch represents a different approach or intermediate step.
Here’s what happens. The AI generates several possible “thoughts” at each decision point. These thoughts are like checkpoints where the AI pauses to consider: Is this working? Should I keep going or try something else?
Let’s say you’re planning a product launch. The AI might explore one branch focused on social media, another on partnerships, and a third on direct outreach. At each checkpoint, it evaluates which path looks most promising based on your goals and constraints.
What makes this powerful is the backtracking ability. If the AI realises a branch isn’t leading anywhere useful, it doesn’t force a solution. It steps back to an earlier decision point and explores a different branch. You’re not locked into the first idea that comes up.
The Key Phases of ToT
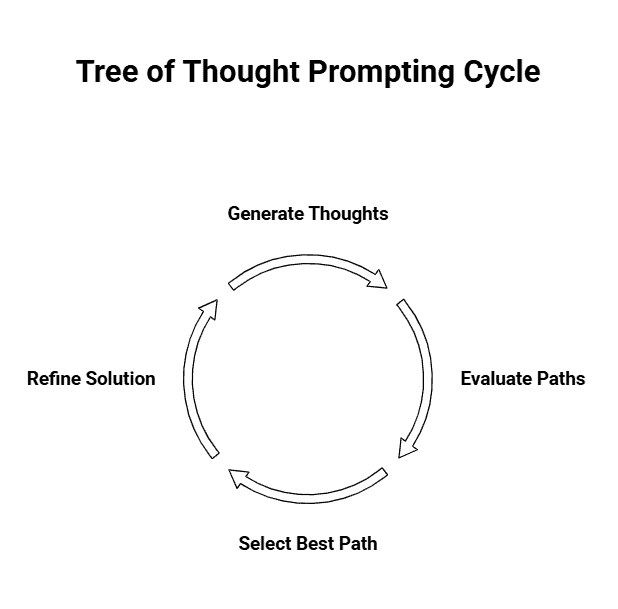
ToT operates through three key phases that work together to find the best solution.
The generation phase creates multiple solution paths. The AI doesn’t settle on one approach. It produces several branches that tackle the problem from different angles. More options mean better chances of finding something that actually works.
Next comes evaluation. The AI assesses each path by weighing strengths, weaknesses, resource requirements, and potential risks. This isn’t about gut feelings. It’s a structured analysis of what each approach offers and what it might cost.
Finally, the selection phase picks the most promising route. The AI ranks options based on feasibility, impact, and risk versus reward. You get a clear recommendation with reasoning behind it, plus suggestions for refining the chosen approach.
Tree of Thought vs Chain of Thought Prompting
Think of Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting as walking down a single path. You take one step, then another, moving from A to B to C in a straight line. It’s the AI showing its work, explaining each step as it goes.
Tree of Thought works differently. Instead of committing to one path, it considers multiple routes at the same time. Say you’re planning a weekend trip. CoT would pick one destination and work out all the details for that choice. ToT would simultaneously explore beach, mountain, and city options, evaluate each one, then pick the best fit.
Here’s what makes ToT stand out. If CoT realises halfway through that its reasoning isn’t working, it’s already committed to that path. ToT can backtrack. It can say, “This approach isn’t panning out,” and switch to a more promising route without starting over from scratch.
The trade-off? CoT is faster and simpler. ToT takes more processing power because it’s essentially thinking through several possibilities before settling on an answer.
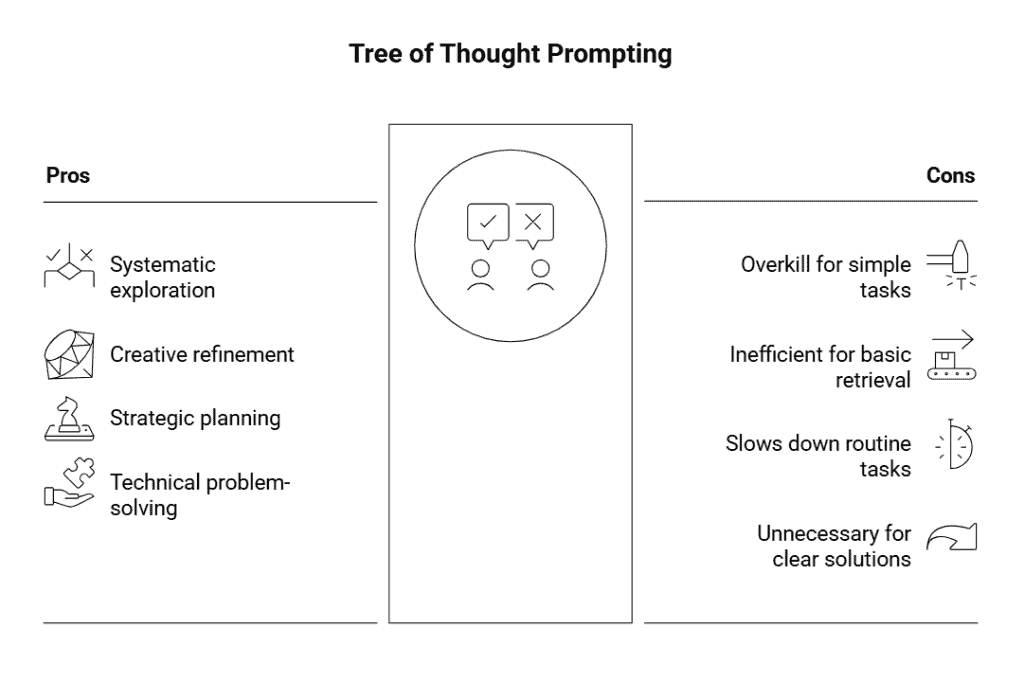
When To Use Tree of Thought Prompting
Tree of Thought (ToT) works best for problems that require exploration, comparison, and step-by-step reasoning. If the task has multiple possible paths or outcomes, ToT helps evaluate them systematically instead of settling for the first idea.
Use ToT when:
- You’re developing a marketing strategy and need to compare audience segments, messaging angles, or channel options.
- You’re working on creative projects (e.g., product descriptions) and want multiple angles, technical, emotional, comparative, to evaluate and refine the best one.
- You’re doing strategic planning such as mapping project timelines with dependencies, constraints, or potential risks.
- You’re solving technical problems like debugging or diagnosing system issues where multiple hypotheses need to be tested.
When NOT To Use Tree of Thought Prompting
ToT isn’t useful for straightforward, factual, or quick tasks. If the question has one clear answer or the task doesn’t require exploring alternatives, ToT becomes unnecessary and time-consuming.
Avoid ToT when:
- You’re asking simple factual questions (e.g., capital of France, Celsius to Fahrenheit).
- You’re retrieving basic information, summarising text, or extracting data from documents.
- You need fast results for routine tasks like drafting simple emails or generating basic content variations.
- The problem genuinely has one obvious solution path and exploring alternatives doesn’t add value.

How To Write Tree of Thought Prompts
Writing a ToT prompt isn’t complicated, but it does require more structure than your typical AI request. You’re essentially building a framework that guides the model through exploration, evaluation, and decision-making. Here’s how to structure it.
Step 1: Define The Problem Clearly
Start by framing exactly what you need solved. The clearer your problem statement, the better your solution paths will be.
Include the context that matters. What’s your goal? What constraints are you working with? What’s the scope?
Compare these two approaches:
Vague: “Help me improve my website.”
Clear: “I need to reduce my website’s bounce rate, which is currently 68%. My budget is $5,000, and I can’t do a complete redesign. The site is an e-commerce store selling outdoor gear.”
The second one gives the AI something concrete to work with. It knows the goal, the limitation, and the context.
Step 2: Request Multiple Solution Paths
This is where you trigger the branching. You need to explicitly tell the model to generate different approaches, not just variations of one idea.
Use phrases like: “Generate three distinct strategies” or “Provide multiple approaches that differ in their core methodology.”
The keyword here is “distinct.” You want genuinely different paths. If you’re planning a marketing campaign, you don’t want three versions of social media ads. You want one path exploring social media, another considering email marketing, and maybe a third looking at partnership opportunities.
Step 3: Set Evaluation Criteria
Tell the model how to judge these options. What makes one solution better than another?
Your criteria should match your situation. That might include cost, time to implement, potential ROI, risk level, resource requirements, or scalability.
Be specific. Instead of “consider feasibility,” try “evaluate based on implementation time and whether it requires hiring additional staff.”
Step 4: Guide The Selection Process
Finally, structure your prompt to compare the options and recommend the strongest one.
Ask the model to rank the approaches against your criteria. Then request a recommendation with reasoning. Something like: “Based on these factors, which approach offers the best balance of quick results and long-term impact?”
This step turns exploration into action. You’re not just collecting ideas. You’re getting a reasoned recommendation you can actually use.
Tree of Thought Prompting Examples
Seeing ToT prompting in action makes the whole approach click. Here are three complete examples that show how you’d actually structure these prompts for different scenarios.
Example 1: Strategic Business Decision
Let’s say you’re deciding how to handle a sudden competitor price drop that’s affecting your sales.
“We’re facing a 20% price cut from our main competitor that’s impacting our Q3 sales. I need to evaluate our response options. Generate three distinct strategic approaches we could take: one focused on matching their pricing, one focused on adding value without changing price, and one focused on repositioning entirely. For each approach, break down the immediate actions, resource requirements, and potential risks. Evaluate each strategy against these criteria: impact on profit margins, customer retention likelihood, and implementation speed. Consider that we have a 6-week timeline and a $50K budget for changes. Based on this analysis, recommend which path makes the most sense and explain why the other options fall short.”
This prompt walks through all four elements. You’ve defined the specific problem (competitor pricing), requested distinct paths (three different strategies), set clear evaluation criteria (margins, retention, speed), and asked for guided selection with reasoning.
Example 2: Creative Content Planning
You’re planning a campaign for a sustainable clothing brand targeting Gen Z.
“I’m developing a social media campaign for our sustainable clothing line aimed at 18 to 25 year olds. The goal is driving website traffic and building brand awareness. Generate three different creative directions: one leveraging user-generated content, one built around educational sustainability content, and one focused on influencer partnerships. For each direction, outline the content types, posting frequency, and key messaging angles. Evaluate these options based on production feasibility with a two-person team, potential reach within our target demographic, and authenticity alignment with our brand values. Our campaign runs for 8 weeks with minimal paid promotion budget. Recommend which direction gives us the strongest foundation and explain what makes the other approaches less suitable for our constraints.”
You’re not just asking for ideas. You’re exploring specific creative paths, setting real-world evaluation criteria, and asking the AI to weigh trade-offs based on your actual limitations.
Example 3: Technical Problem-Solving
Your web app is experiencing slow load times during peak hours.
“Our web application is experiencing 8 to 12 second load times during peak traffic hours, affecting user experience and causing drop-offs. Explore three different technical solutions: optimising database queries and indexing, implementing a caching layer, and moving static assets to a CDN. For each solution, detail the implementation steps, estimate the development time, and identify potential complications. Evaluate these approaches based on expected performance improvement, development complexity for a small team familiar with Node.js and PostgreSQL, and ongoing maintenance requirements. We need to implement a solution within 3 weeks. Recommend which approach addresses our bottleneck most effectively and explain why the alternatives are less optimal given our technical stack and timeline.”
This shows how ToT works for technical decisions. You’re exploring different solutions, not just asking for the answer, and you’re making the AI consider your specific technical environment and constraints.
Benefits of Tree of Thought Prompting
Tree of Thought (ToT) prompting stands out because it forces exploration before decision-making. Instead of jumping to the first acceptable answer, it lets you compare multiple reasoning paths side by side. This leads to deeper thinking and more reliable outcomes.
- It helps you explore a wide range of possible solutions instead of defaulting to the first idea.
- It improves decision quality on complex problems by evaluating different paths against clear criteria.
- Research shows ToT improves reasoning accuracy due to its transparent comparison of alternatives.
- It prevents anchoring bias by ensuring multiple branches are developed before choosing a final direction.
You end up with a more considered, defensible final answer that reflects real exploration rather than guesswork.
Limitations of Tree of Thought Prompting
While powerful, ToT prompting isn’t always the most efficient. It requires more steps, more structure, and more computational resources. For simpler or time-sensitive tasks, this complexity quickly becomes unnecessary.
- It consumes significantly more tokens and time because the AI must generate, evaluate, and combine multiple branches.
- It requires well-designed prompts with clear branch definitions and evaluation criteria, or the output becomes scattered.
- It’s overkill for simple tasks like definitions, direct facts, or basic calculations.
- Sometimes ToT produces several strong paths but no clear winner, leaving you to make the final judgment.
In short, ToT works best when complexity justifies the effort. If the task is straightforward, or you need quick answers, simpler prompting will serve you better.
Best Practices For Tree of Thought Prompting
Start with three paths. That’s the sweet spot for most problems. You get enough diversity to avoid tunnel vision without drowning in options. If the problem turns out to be more complex than expected, you can always adjust.
Make your evaluation criteria specific and measurable. Don’t just say “evaluate based on feasibility.” Say “evaluate based on implementation time, budget under $10k, and technical complexity for a team of two developers.” The more concrete your criteria, the sharper your results.
Balance depth with efficiency. Not every branch needs to go five levels deep. Sometimes two levels of exploration give you what you need. Think about the actual complexity of your problem before deciding how elaborate to make your tree.
Test your prompt structure with a simpler version of your problem first. You’ll learn quickly if your evaluation criteria make sense or if your branch definitions are too vague. Iterate based on what you see.
Know when to use simpler methods. If you’re halfway through crafting a ToT prompt and realise a straightforward Chain of Thought would work fine, switch gears. Save ToT for problems that genuinely benefit from exploring multiple paths.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.

![Tree of Thought Prompt Generator [Free & AI Powered] Tree of Thought Prompt Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Cover-images-3-150x150.webp)
![Chain of Thought Prompt Generator [Free & AI Powered] Free Chain Of Thought Prompt Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Copy-of-Cover-images-4-150x150.webp)

![Reasoning Prompt Generator [Free & AI Powered] Free Reasoning Prompt Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Copy-of-Cover-images-1-150x150.webp)
![Zero Shot Prompt Generator [Free & AI Powered] AI Zero Shot Prompt Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/AI-Zero-Shot-Prompt-Generator-150x150.webp)

![Few Shot Prompt Generator [Free & AI Powered] AI Few Shot Prompt Generator](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/AI-Few-Shot-Prompt-Generator-150x150.webp)

