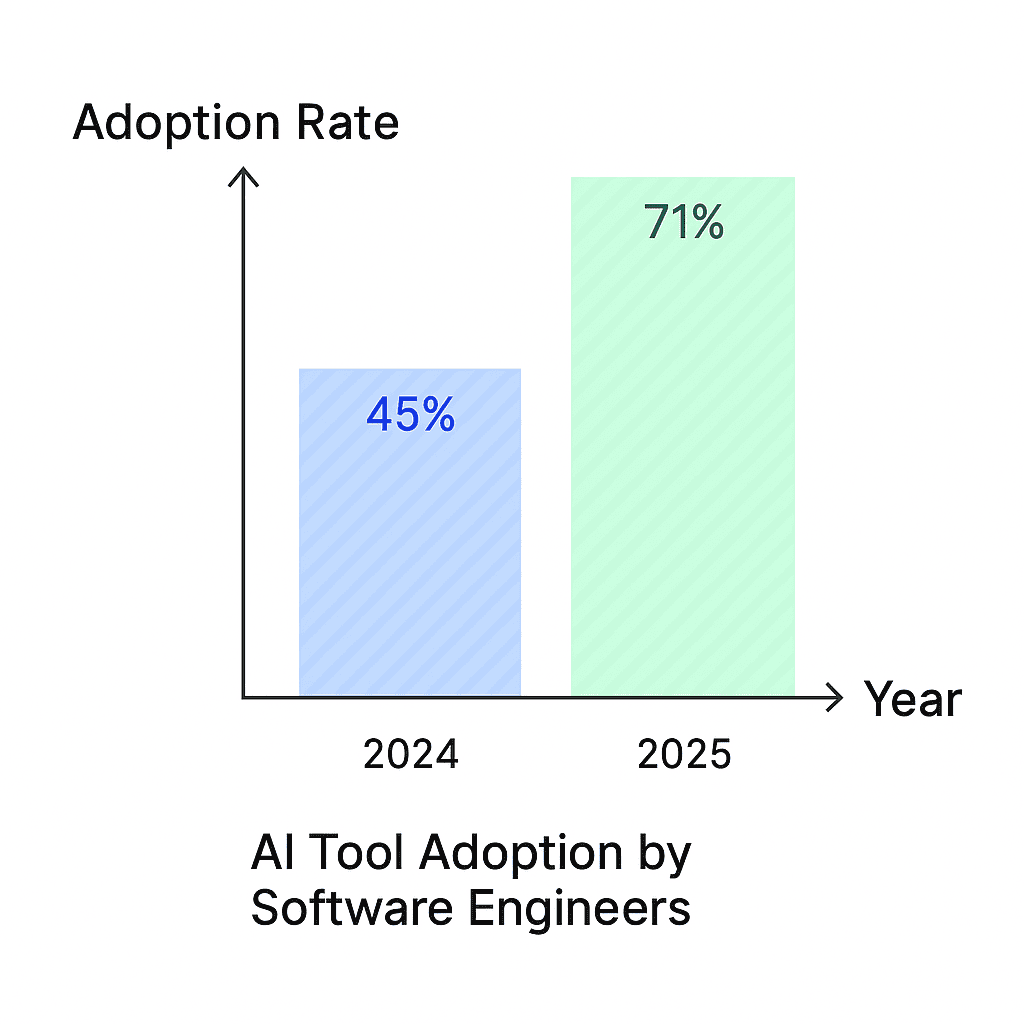
71% of engineers now use AI tools in 2025, up from 45% in 2024. That jump happened in just one year.
AI is changing how software gets built. The tools are faster. The workflows are different. And people are asking the obvious question: will AI replace software engineers?
The answer isn’t simple. AI can do a lot, but it can’t do everything. Let’s break down what’s actually happening in software engineering and what it means for the people who build software for a living.
Software Engineering Before AI
Software engineers used to write every line of code manually. Writing boilerplate code for APIs, setting up database connections, and creating repetitive functions ate up hours of their day.
Debugging meant reading through code line by line. You’d set breakpoints, check variable values, and trace execution paths manually. Finding that one misplaced semicolon could take half a day.
When stuck on a problem, engineers turned to Stack Overflow. They’d search through documentation, read forum threads, and test different solutions until something worked. The research process alone could stretch a simple fix into an afternoon task.
Testing followed a similar pattern. Engineers wrote unit tests by hand, ran test suites, and reviewed results. Code reviews meant reading through pull requests manually, checking for bugs, style issues, and logic errors. Senior developers spent significant chunks of their week just reviewing other people’s code.
This workflow worked, but it was slow. Repetitive tasks filled up calendars. The actual creative problem solving got squeezed between all the routine work.
How AI Has Changed Software Engineering?
What changed most is speed. Tasks that took half a day now take minutes. According to Netguru, 78% of organisations now use AI in at least one business function, and software engineering is leading that shift.
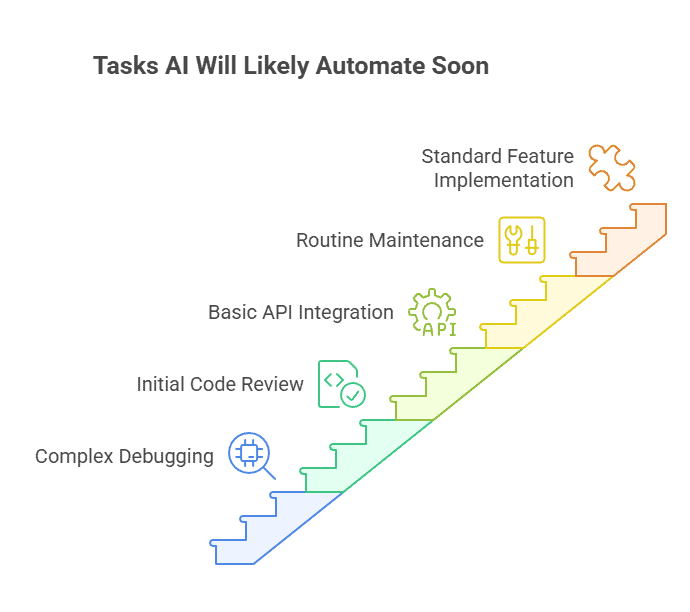
Tasks AI Has Completely Automated
Some coding tasks barely need human hands anymore. AI tools handle them from start to finish without breaking a sweat.
- Boilerplate code generation. You type a function name and AI writes the entire template. What used to take 10 minutes now happens in seconds.
- Syntax error detection. Your editor catches mistakes before you even finish typing. Red squiggly lines appear instantly. You fix them on the spot.
- Code formatting and linting. No more arguments about tabs versus spaces. AI formats everything according to your style guide automatically.
- Basic documentation generation. AI reads your code and writes comments that actually make sense. It explains what functions do and what parameters mean.
- Simple bug fixes. Missing semicolon? Wrong variable name? AI spots these issues and suggests fixes before you even run the code.
- Code translation between languages. Need to convert Python to JavaScript? AI handles the syntax changes and adapts the logic to match each language’s conventions.
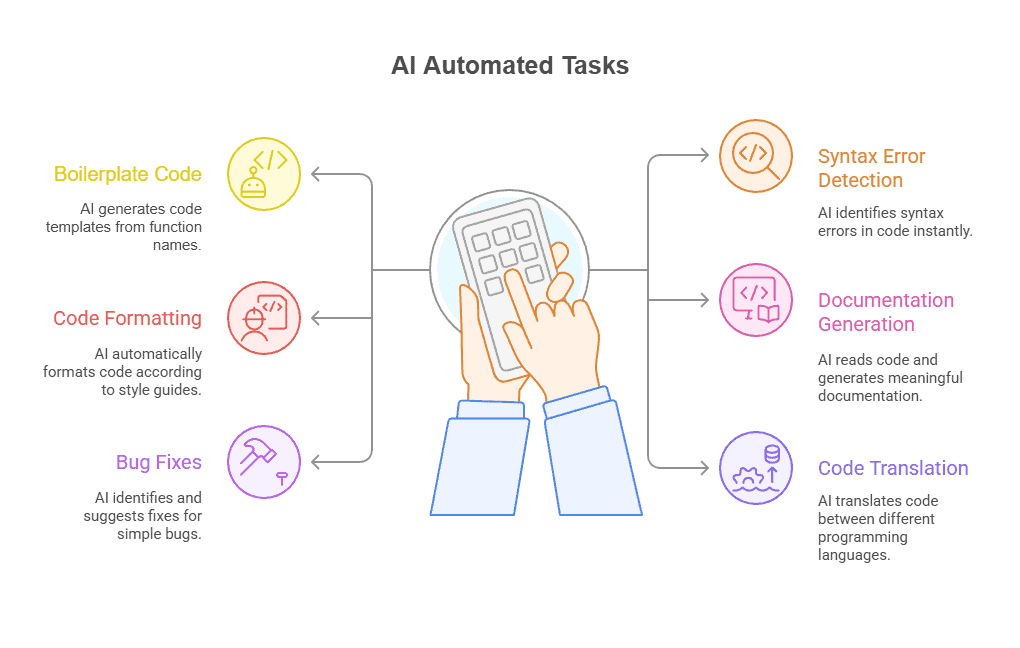
Tasks AI Will Likely Automate Soon
AI isn’t finished evolving. While some tasks still need human judgment, the gap is shrinking, which is why people increasingly ask will AI replace software engineers.
1. More complex debugging scenarios. AI can already spot simple bugs. Soon it’ll track down the weird ones that happen only on Tuesdays when the database is under load.
2. Initial code review passes. AI will scan pull requests for logic errors, security issues, and performance problems before a human ever looks at them.
3. Basic API integration. Connecting to third-party services means reading docs and writing authentication code. AI will soon handle standard integrations from scratch.
4. Routine maintenance tasks. Version updates, dependency management, and compatibility fixes. AI will take care of these without anyone asking.
5. Standard feature implementation. Common features like user authentication, search bars, and pagination. AI will build these based on specifications alone.
What AI Cannot Do in Software Engineering
AI can’t understand why your company chose that weird database structure five years ago. It doesn’t know that the CEO hates pop-ups or that your biggest client needs a specific workflow.
Here’s what still needs human engineers:
- Business context and user needs. AI doesn’t sit in meetings where someone explains that customers actually want X, not Y. It can’t read between the lines when a stakeholder says “make it simple” but really means “don’t change what my team already knows.”
- Architectural decisions. Choosing between microservices and a monolith isn’t just technical. It depends on your team size, budget, timeline, and what happens if the system goes down at 3 AM. AI struggles with this kind of complexity and the trade-offs that come with real-world constraints.
- Legacy systems with tribal knowledge. That module everyone’s afraid to touch because Bob wrote it in 2009 and he’s the only one who knows why it’s built that way? AI can’t decode that without the story behind it.
- Stakeholder communication. Explaining to a non-technical manager why the “quick fix” they want will break everything takes human judgement and patience.
Current AI Adoption Rates Among Software Engineers
In 2024, around 45% of developers used AI tools regularly. By 2025, that number shot up to 71%. That’s a 26-percentage-point increase in just one year. What pushed this surge? The tools got better at understanding context.
Common AI Tools Software Engineers Use Now
Here’s what most developers have open in their tabs:
- GitHub Copilot writes code alongside you inside your editor. It reads what you’re building and suggests the next lines before you type them.
- ChatGPT answers coding questions, explains complex functions, and helps debug when you’re stuck on something weird at 2 AM.
- Tabnine learns your coding style and autocompletes based on patterns it picks up from your work.
- Amazon CodeWhisperer (now called Amazon Q Developer) works best if you’re coding in the AWS environment, suggesting code that fits their cloud services.
- Replit Ghostwriter handles everything from writing to debugging right inside the browser-based Replit platform.
What Software Engineers Are Most Worried About
The tools are helpful, but they also make people nervous. According to Exploding Topics, 43% of workers expect AI to cause job changes in the next five years. For developers specifically, here’s what keeps them up at night:
- Job security: If AI writes code faster, will companies need fewer developers?
- Skill degradation: Relying too much on AI might make you forget how to solve problems from scratch.
- Code quality: AI suggestions aren’t always secure or optimised. Blindly accepting them can introduce bugs or vulnerabilities.
- Over-dependence: What happens when the tool goes down or gives bad advice and you can’t spot it?
Job Impact of AI on Software Engineering Roles
Not all software engineers face the same level of risk. The impact depends heavily on where you sit in the career ladder.
Impact on Junior Engineers
Entry-level roles are taking the biggest hit. Companies are hiring fewer junior developers because AI can handle many tasks that used to go to new graduates. Code reviews, bug fixes, simple feature implementations, these were once training grounds for juniors. Now they’re prompts.
That means new engineers need to show value beyond just writing code. You’ll need stronger problem-solving skills and the ability to work with AI tools from day one. The bar for entry has risen.
Impact on Senior Engineers
Senior developers? Less threatened. Your value isn’t in typing code faster, it’s in knowing what to build and why. AI doesn’t understand user needs, business constraints, or technical trade-offs the way someone with years of experience does.
Your work is shifting toward more strategic territory. System design, architecture decisions, mentoring, cross-team collaboration. McKinsey’s State of AI 2025 shows organisations are still figuring out AI’s workforce impact, but one pattern is clear: jobs requiring judgment and experience remain critical.
What Software Engineers Should Do to Stay Relevant
Here’s what actually matters if you want to stay valuable:
- Learn to work with AI tools. You don’t need to become an AI expert, but you should know how to use code assistants effectively. They’re part of the job now.
- Focus on problem-solving, not syntax. Understanding the why behind code matters more than memorising how to write it. AI handles syntax. You need to handle logic and architecture.
- Get better at communication. You’ll spend more time explaining problems, reviewing AI-generated code, and collaborating with non-technical teams. Writing and talking clearly become bigger parts of your job.
- Understand the business side. Engineers who grasp customer needs, revenue models, and business constraints are harder to replace. You’re not just coding you’re solving business problems.
- Go deeper into system design. High-level architecture, scalability decisions, security considerations these require experience AI doesn’t have. Double down on these skills.
Will AI Replace Software Engineers?
No, but AI will replace software engineers who refuse to adapt.
AI isn’t eliminating the profession, it’s changing what the job looks like. The engineers who survive are the ones who use AI as a tool rather than compete with it. Code generation is getting automated. Problem definition, system design, and business translation aren’t.
Ten years from now, there will still be software engineers. They’ll just spend less time writing boilerplate and more time on the complex, messy, human parts of building software. The role isn’t disappearing. It’s evolving.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.









