John has recently started working for Growth Enterprises as a General Production Manager. He was asked by Sean, the CEO of the firm, to coordinate with the Factory Production Manager to ensure that the company meets the deadline for the order delivery for one of its oldest clients. He was confused as to why he was asked to coordinate with the Factory Production In-charge when his boss could himself connect with them.
He asked his friend Raven, who told him that Sean had to look after other things in the organisation as well. Allocating work to his juniors allows him to assign responsibility for each task, thus defining the authority of the employees to form a hierarchy that makes managing everything easy.
Every organisation needs a hierarchy to establish a chain of command in order to ensure its efficient working. This chain of command is used to define the level of authority and responsibility that is tied to every position in an organisation. Levels of management help in providing this clarity.
What Are The Levels Of Management?
Levels of Management refer to the line of demarcation among the employees in an organisation on the basis of the authority and responsibility allocated to them.
Two important phrases in this definition are:
- Distinction made among the employees: Every employee in an organisation works on a different set of things in order to achieve the collective objective of the organisation. They are assigned different jobs and allocated varied amounts of responsibility.
- Basis of authority and responsibility: The distinction between the employees is made on the basis of their right to give orders and assign duties to their subordinates as well as their obligation to complete the job assigned to them on time.
Why Are Levels Of Management Important?
Levels of management help in ensuring the presence of effectiveness and efficiency in the work done in the organisation.
There are many functions that need to be handled simultaneously in an organisation. One person cannot handle it all. So, the work is divided amongst the employees according to their skills, experience, and post in the organisation. Each manager is expected to look after a certain part of the organisation’s work and oversee his/her subordinates to fulfil his responsibility towards the company.
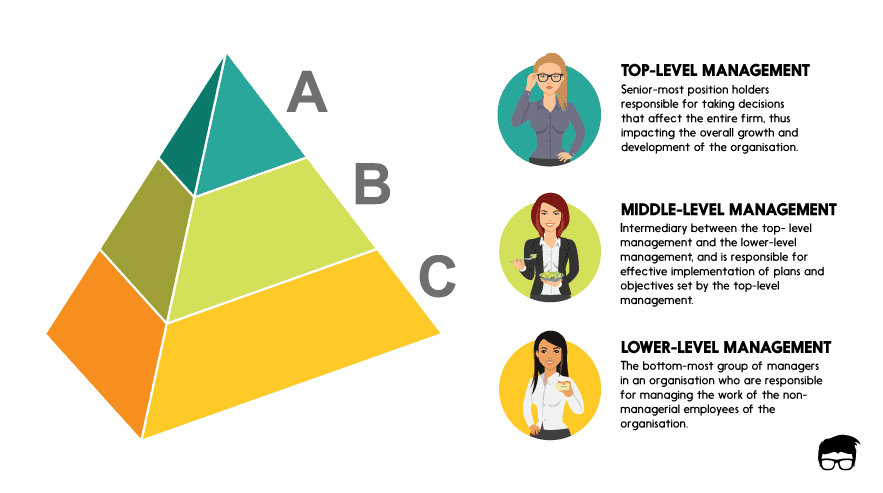
The 3 Levels of Management
A traditional organisation is generally split into three levels:
- Top-level management,
- Middle-level management, and
- Lower-level management.
The authority and level of responsibility of the managers in each of these levels reduce as we move down the ladder.
Normally, these levels are represented in the form of a pyramid having many lower-level managers, fewer middle-level managers and the lowest number of managers at the top level of management.
What Is Top-Level Management?
The top-level management refers to the senior-most position holders responsible for taking decisions that affect the entire firm, thus impacting the overall growth and development of the organisation. They are accountable to the shareholders and the general public.
What Titles Does The Top-Level Management Hold?
Top Level Managers normally occupy the position of Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Financial Officer (CFO), Chief Operating Officer (COO), President, Executive President, Managing Director and other such high-ranking sophisticated titles.
What Is The Role Of Top-Level Management?
The top-level management ensures the smooth working of the organisation as a whole. They are responsible for making sure that the overall objective of the organisation is achieved. Their role can be divided into the following 4 categories:
- Set Goals and Objectives for the Organisation: The primary and the most important role of top-level management is to set goals and objectives for the organisation as a whole. This means that the top-level managers don’t limit their thinking to a particular product or a department, they work towards formulating strategic goals for the organisation.
Goals are the long-term milestones that an organisation wishes to achieve or fulfil. Objectives are time-bound, measurable and precise. They help in determining the steps that assist in achieving a particular goal. The main objectives of any organisation are survival, profit and growth. The top-level management helps in defining these objectives in terms of real parameters. - Formulate Policies and Plan of Action: The top-level management formulates policies and guidelines that govern the working of the organisation. It also lays out the long term as well as the short-term plan of action to achieve organisational goals.
Policies define the way in which certain things are done in an organisation. For example, an organisation may have a policy of hiring only experienced candidates. Thus, policies guide the employees in the organisation on how a particular task should be conducted. - Procurement of Resources: The top-level management is also responsible for making sure that all the necessary resources are available as and when required by the firm. This includes financial resources like money, physical resources like machinery and human resources or employees.
- Mediator between the public and the organisation: Top-level management is responsible for all the communication between the public and the organisation. They are the face of the company, representing it at press conferences, social gatherings and other events.
What Is Middle-Level Management?
Middle-level management is an intermediary between the top-level management, who makes the decisions, and the lower-level management, who directs the work of the nonmanagerial workers of the organisation. Middle-level management is responsible for the effective implementation of plans and objectives set by top-level management.
They are mainly grouped on the basis of departments or the divisions they work in. The lower level management is accountable to the middle-level management who in turn are accountable to the top executives.
What Titles Does The Middle Level Management Hold?
Middle-level managers generally earn the title of General Manager, Department Managers like HR Manager, Finance Manager, Community Manager, etc. They can also be divided on the basis of Branches.
What Is The Role Of Middle-Level Management?
The middle-level management is responsible for communicating the goals and objectives set by the top executives to the lower level management and ensuring that the work done by the lower level management aligns with these goals. The role of a middle-level manager can be listed as follows:
- Interprets Plans and Communicating them to Lower Level Management: The middle-level managers interpret the plans and policies set by the top-level management and communicate them effectively to the lower level management so that everyone works towards the set objective.
- Reports Results and Feedback to the Top Executives: The top-level management expects the middle-level management to communicate any feedback from the lower level management to them. They also need to send regular reports to the top-level executives.
- Motivates the Employees: The middle-level management is responsible for motivating the employees to work for the achievement of the organisational goal. They are required to provide continuous support and guidance to help the employees improve their performance so that a positive culture prevails in the organisation.
- Hires and Trains the Employees: The middle-level management is responsible for hiring the best fit for the organisation and training them so that they can reach the level of efficiency as high as that of a regular employee. They also need to evaluate the performance of all the employees at regular intervals.
What Is Lower-Level Management?
The lower-level management is the bottom-most group of managers (also called first-line managers or supervisors) in an organisation who are responsible for managing the work of the nonmanagerial employees of the organisation. They are accountable to the middle-level managers and provide day to day updates of the working in the organisation.
What Titles Does The Lower-Level Management Hold?
Lower-level managers generally go by the name of Supervisor, Foreman, Shift Supervisor, Store Manager and other such positions involving direct communication with the (factory) workers of the organisation.
What Is The Role Of Lower-Level Management?
The lower-level management plays an integral role in an organisation as they are directly involved in the production process. They are familiar with the problems faced by the workers and act as a point of contact between the middle-level management and the workforce. The quality of the production depends on them. The role of lower-level management can be divided into the following points:
- Oversees the workforce: The lower level management is responsible for overseeing the work of the workers and providing guidance to them as and when required. They need to see that the processes handled by the workers are done as per the deadlines given by the middle-level management.
- Maintains Standard and Quality of the work: Since the lower level management is in direct communication with the workers, they can easily help in ensuring that the standard and quality of work is not compromised.
- Improves the Morale of Workers: The lower level management is responsible for improving the morale of the workers and motivating them to work effectively and efficiently. They manage the relationship between the organisation and the workforce, communicating any grievances faced by the workforce to the upper-level managers and solving them to maintain harmony in the organisation.
- Minimises Wastage: The lower level management is responsible for minimising wastage of time, material and efforts during the production process. They are also responsible for maintaining discipline among the workers.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on the levels of management in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.








