As the world shrinks with each passing day, the business opportunities multiply at an ever-increasing rate leading to intense competition. Due to this pressure of survival and growth, organisations must devise and implement a competitive growth strategy to strengthen their economic position.
The Ansoff Matrix is one such framework that aids in formulating an effective growth strategy. In this article, we will discuss what is Ansoff Matrix, its importance, the four strategies associated with it and some examples to understand it better.
What Is Ansoff Matrix?
The Ansoff Matrix, also known as the product/market expansion grid, is a future-oriented portfolio analysis tool marketers use to devise future growth strategies while factoring in the inherent risks associated.
Developed by Igor Ansoff in 1957, the Ansoff model is based on the fundamental question of ‘where should a company direct its growth efforts?’ and provides four distinct growth strategies that a company can adopt, depending on whether it wants to target new markets or new products.
The matrix suggests 4 different growth strategies that can be implemented in the business namely –
- Market penetration [existing product, existing market]: The company tries to grow its existing products’ sales in the existing market. The aim is to increase the market share of the company. For example, Coca-Cola focusing on selling more bottles of Diet Coke in the US market.
- Product development [new product, existing market]: The company tries to develop new products for its existing markets. The aim is to satisfy the changing needs of the customers in the existing market. For example, Samsung launching the new Galaxy phone focused just on the needs of Gen Z.
- Market development [existing product, new market]: The company tries to enter new markets with its existing products. The aim is to increase sales by selling the same product in a new market. For example, Google focusing on the Chinese market.
- Diversification [new product, new market]: The company enters a new market with a new product. The aim is to reduce the risk by spreading the business into new areas. For example, Apple launching a home theatre system for Indian customers.
The 4 Strategies Of The Ansoff Matrix
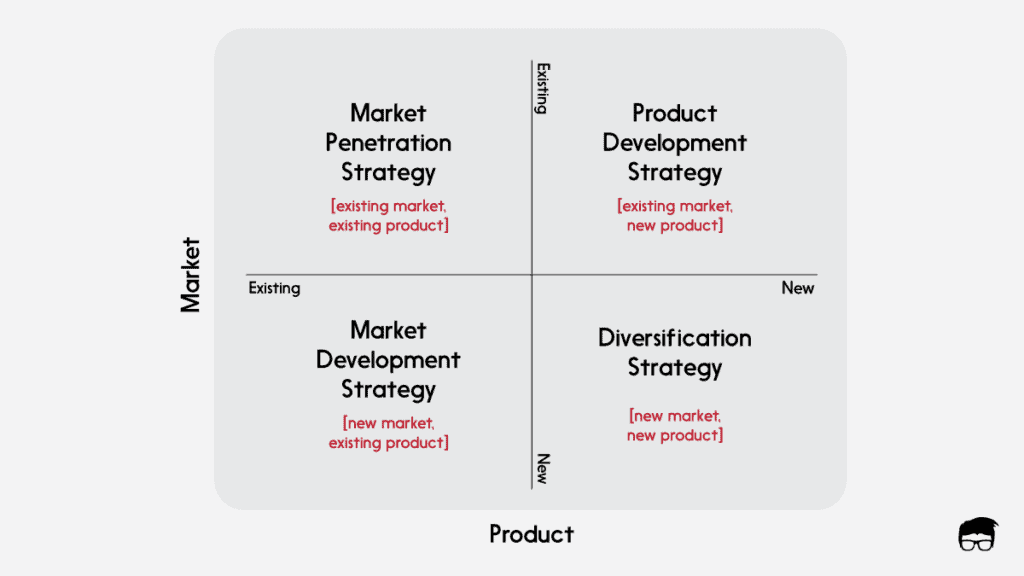
Product and market are the most important factors driving business growth. The Ansoff Matrix factors in both aspects to create a 2-dimensional matrix that gives rise to 4 growth strategies.
Market Penetration
Market penetration is a measure of how much an offering is bought by customers as compared to the total estimated market.
This is the most commonly used strategy wherein the company focuses on selling more of its current products to its current markets. This can be achieved by either improving marketing efforts or providing customers with additional benefits that encourage them to buy more. For example, a mobile phone company may offer more minutes or data at a lower price to attract new customers and encourage existing customers to buy more.
What Is The Goal Of A Market Penetration Strategy?
The goal of a market penetration strategy is to increase sales of a company’s products or services in the existing market without changing the product. This is usually done by increasing marketing efforts and improving customer service.
For example, a company may offer discounts or special deals to customers in order to increase sales. Additionally, the company may invest more in advertising and promotion to increase brand awareness and reach more potential customers.
When Is A Market Penetration Strategy Used?
The market penetration strategy is used by firms when they don’t have any new product or service to launch or any new market to explore but still wish to expand their revenue and market share. Companies usually adopt this strategy in the early stages of their product life cycle when they are still trying to gain a foothold in the market.
How To Use A Market Penetration Strategy?
There are various ways in which a company can go about adopting a market penetration strategy. Some of the most common methods are as follows:
- Price Reduction: By reducing prices, companies make their products and services more affordable and thus attract more customers. This strategy is particularly effective in markets where the price is a major deciding factor for customers.
- Advertising and Promotion: Advertising and promotion can help create awareness about a company’s products and services and make them more attractive to potential customers.
- Improved Distribution: By incorporating new distribution channels or improving existing ones, companies can make their products and services more accessible to customers.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Mergers and acquisitions involve combining two or more companies to create a new entity. This strategy can help companies expand their reach and increase penetration in the current market.
Risks Associated With Market Penetration Strategy
The main risk associated with market penetration strategy is that of becoming complacent. Companies that have successfully penetrated their markets may become overconfident and stop innovating. This can lead to them losing their competitive edge and eventually being replaced by newer, more agile firms.
Product Development
The product development strategy is where a firm introduces a new and improved product line in its existing market.
The main aim of this strategy is to maintain market share and generate new revenue streams by offering customers something new that they value.
In order to successfully implement a product development strategy, companies need to deeply understand their target market and what they are looking for.
An excellent example of a company that has successfully used a product development strategy is Apple. Starting as a computer company, it has expanded its product range to include iPods, iPhones, iPads, and a host of other electronic devices.
What Is The Goal Of A Product Development Strategy?
The main goal of a product development strategy is to create new products or services that appeal to customers and generate new revenue streams for the company in the existing market.
Product development can also help companies to stay ahead of the competition by constantly innovating and offering new products or services that the competition does not have.
When Is A Product Development Strategy Implemented?
The product development strategy is implemented when the company has an established large customer base and the market for its existing products is on the brink of saturation.
This involves high inherent risk as it demands a huge investment from research and development to build a new product.
However, it’s easier to market a new product to an existing customer base as they are already aware of the company and its products.
How To Use A Product Development Strategy?
The organisation focuses on building a differentiated product to improve its product portfolio and operate on the customer’s brand loyalty. The courses of action include:
- Investing in research and development to provide better and cost-efficient solutions.
- Merging resources with competitors to save time and effort in research.
- Forming strategic partnerships to acquire rights to sell a product developed by another company.
Risks Associated With Product Development Strategy
The risks associated with product development strategy are:
- Developing a new product takes a lot of time, effort, and resources.
- The success of the new product is uncertain as it needs to be accepted by the customers.
- The new product can cannibalise the sales of the existing products.
Market Development
The market development strategy is adopted to target new markets with the existing products.
For example, a company selling tennis shoes in the domestic market may decide to target foreign markets.
Another example would be a company selling healthy snacks to working professionals, targeting the same to students in college canteens. Here, the company would not be introducing any new product but targeting a new market segment.
What Is The Goal Of A Market Development Strategy?
Businesses aim to reach a wider audience and expand their user base by selling their offerings in previously unexplored markets. This makes way for acquiring new customers and acts as a driving force for growth and increased revenue.
When Is A Market Development Strategy Implemented?
A business generally uses a market development strategy when its existing market has reached a saturation point, and they are not ready to launch a new product.
The focus is on existing products, so it does not require a huge investment in product research and development, resulting in low business risk. So this strategy best works for a business that is not willing to take risks at the moment.
How Is A Market Development Strategy Implemented?
The strategy concentrates on taking the existing product to a new market. Here’s how they implement it:
- Entertaining a different customer segment in the same geographic area
- Expanding markets geographically i.e. domestically and internationally
Risks Associated With Market Development Strategy
The main risk involved in this strategy is that the company may not understand the needs of a new market and thus, the product may not be accepted. Also, it is difficult to forecast demand in a new market.
Another risk is that the company may incur a lot of costs to enter a new market. This is because they would need to research, develop new marketing strategies and create awareness about their product.
Diversification
A diversification strategy is a market strategy where the business focuses on selling a new product to a new market and involves entirely different skills, technology and knowledge.
The risks are much higher as the company is starting from scratch. This strategy is generally adopted by companies that have spare cash and want to enter a new business.
An example of a company that has used this strategy is Google. It started with the search engine and then moved into selling mobile phones (Pixel), home appliances (Nest) and even forays into self-driving cars.
What Is The Goal Of A Diversification Strategy?
Businesses generally implement diversification strategies to reduce their reliance on a single line of products while gaining a synergetic advantage to sell more of their existing product by adding a new product.
When Is A Diversification Strategy Implemented?
Diversification acts as a means to utilise the spare capacity of the business more efficiently and effectively by developing a new line of products.
It is the riskiest strategy in the matrix as it demands both product and market development on the part of the business and focuses on an entirely new revenue stream. But with the increased risk it also offers the opportunity for huge returns.
How Is A Diversification Strategy Implemented?
The management has mainly two different approaches when it comes to implementing diversification strategies.
- Related diversification: The marketing strategy where the business enters into a new industry by exploiting brand name, sales and distribution capacity and marketing skills as the new product has some similarities with the existing products. For example, Apple, a technology company, introduced AirPods when it was already established in the smartphone industry.
- Unrelated diversification: The marketing strategy where a business invests in a new product portfolio and employs different technologies where it’s unlikely to have any similarities between the new and existing products. For example when Coca Cola a soft drink company, acquired Columbia Pictures, a movie studio, in 1982.
Companies use related diversification to mitigate their risk and use unrelated diversification to reduce risk by operating in multiple industries.
Risks Associated With Diversification Strategy
The main risks associated with diversifying into new products or services are:
- Difficulty in managing multiple products and businesses: If a company has a wide range of products and businesses, it can be difficult for managers to keep track of everything and make sure that each business is profitable.
- Lack of focus: A company that is diversified into too many different areas may lack focus and could end up spread too thin.
- Increased complexity: A diversified company is likely to be more complex than a single-business company, making it more difficult to manage and understand.
The Importance Of The Ansoff Matrix
Companies with multiple offerings large enough to be categorised into SBUs (Strategic Business Units) face the problem of correct resource allocation. Ansoff Matrix provides a framework for resource allocation and developing marketing plans. It forces the company to consider the risks inherent in its growth strategy.
Moreover, designing a strategy involves a careful analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the company to fit the external opportunities and threats present in the market. Once an organisation has derived its results from the SWOT analysis, it needs to channel them into individual strategies and choose a business model. Ansoff Matrix helps the business to choose one such model.
The Ansoff Matrix is simple to understand and gives an overview of all possible alternatives. It is best suited for organisations operating in multiple industries. The business can choose the best strategy based on its requirements and risk-taking capacity.
Bottom Line?
Each company has its own method of analysing its business position and choosing a business strategy for growth and development in the market. Several tools are available that aid the process of identifying, analysing and choosing from alternatives much easier.
Risk cannot be totally eliminated from a business. The solution is to choose the right strategy at the right time, and using a portfolio analysis model like the Ansoff Matrix, it becomes much easier to make decisions.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on Ansoff Matrix in the comments section.
A startup enthusiast, optimist and full time learner. With keen interest in finance and management, Khushi believes communication to be the key to every management. Always ready to explore more and walking that extra mile in putting efforts.









