There was a time when you had to face the hassle of going to the grocery store every time you needed something, or rush to a pharmacy or stand in a line at a cafe or restaurant to buy some food for yourself. It wasn’t easy to even imagine a day when all these things would arrive at your doorstep with just a few taps on-demand.
A perfect utopia a decade back is a reality now.
This is what the hyperlocal business model is all about – making the consumers’ life easy by building a local ecosystem that fulfils needs on-demand. Poised to grow by a whopping $451.64 million in the coming years, it has an expected CAGR of 18% during the forecast period.
Wondering what a hyperlocal business model is, how it works and makes money?
Fret not!
Here’s a guide that explains it all.
What Does Hyperlocal Mean?
Hyperlocal’ or extensively local literally means a well defined and specific community and geographical area. In its essence, it is localisation in its true spirit. It focuses on a highly specific location and community, with geography and time as the key factors. For instance, a neighbourhood or specific locality of some state of a country would be termed hyperlocal.
Since it is based on personalised one to one services, hyperlocal works for specific areas. It also has the ability to cater to well-defined needs in an effective and efficient way using modern technology.
What Is Hyperlocal Business Model?
A hyperlocal business model, also known as a micro-marketplace, is a business that focuses on the needs of geographically local consumers. It aims to fill in the gap between demand and supply with an efficient network of suppliers/vendors who fulfil consumer demands by selling them what they need at their doorstep.
Technically, a hyperlocal business model is an online business model that caters to customers’ on-demand needs, which are met through a local ecosystem.
In other words, the customer uses a platform or service aggregator that acquires the requested product locally and delivers it to the customer’s doorstep in the respective geographical location. Grocery shopping, food delivery, health care, and many other services have taken a different dimension altogether with the ushering of hyperlocal e-commerce platforms.
The unique selling proposition of the hyperlocal business model is its ability to get good quality products and services delivered at peoples’ doorsteps at unbelievably fast speeds. Using digital platforms makes it more convenient for the customers to monitor the entire process and keep track of deliveries in real-time.
A hyperlocal business model usually has the following characteristic features:-
- It is a keen-eyed and personalised business that focuses on the needs of geographically local consumers.
- It targets a specific area with a high demand for goods and services.
- It caters to the well-defined needs of people in an effective and efficient way using modern technology
- The unique selling proposition of this business model is its ability to get good quality products and services delivered at people’s doorsteps at unbelievably fast speeds
- An effective mix of the marketplace and aggregator business model.
Technologies such as GPS (Global Positioning System), mobile applications, and social media play a prominent role in the hyperlocal business model. This combination makes it more convenient for the organisers to monitor the entire process and keep track of deliveries.
How Does A Hyperlocal Business Operate?
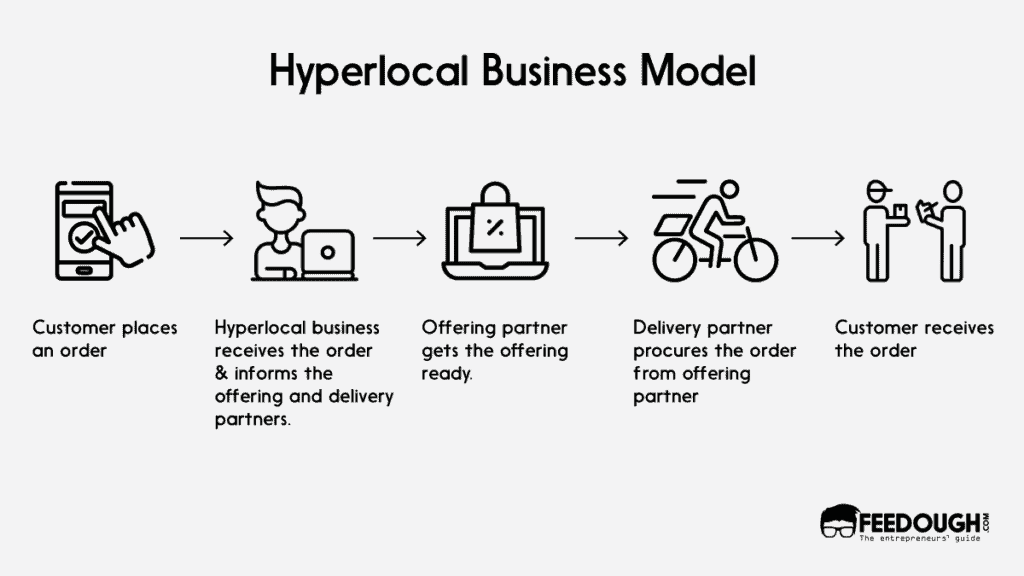
The hyperlocal businesses work with the pre-existing infrastructure and elements of local markets but connect them all in an ecosystem where orders can be taken, processed, procured and eventually delivered, all in one place. It operates with the help of offering and delivery partners to bridge the gap between customer demands and retail supplies.
Businesses operating under the hyperlocal business model provide online retail platforms to local consumers and businesses. They usually have an inventory database where all the information is stored about the products, services, customers and locations. They also have an ordering platform through which the customers can order products and services.
To understand it better, let us consider an example of a hyperlocal on-demand food platform. When a customer places an order for a required food item through the platform, the platform receives that order and passes on the details to the offering partner (local store) and the delivery partner (delivery person). The delivery partner then procures the required food item from the local business and delivers it to the customer’s specified location. The platform drives the entire process and earns a commission for the role it plays and the local stores get amplified visibility and delivery services in the process.
The biggest reason for the success of hyperlocal businesses is their ability to generate revenue through a variety of business models. However, it depends on the nature and type of offering being offered by a particular hyperlocal platform.
In general, hyperlocal brands operate on four business models:
Inventory-Led Model
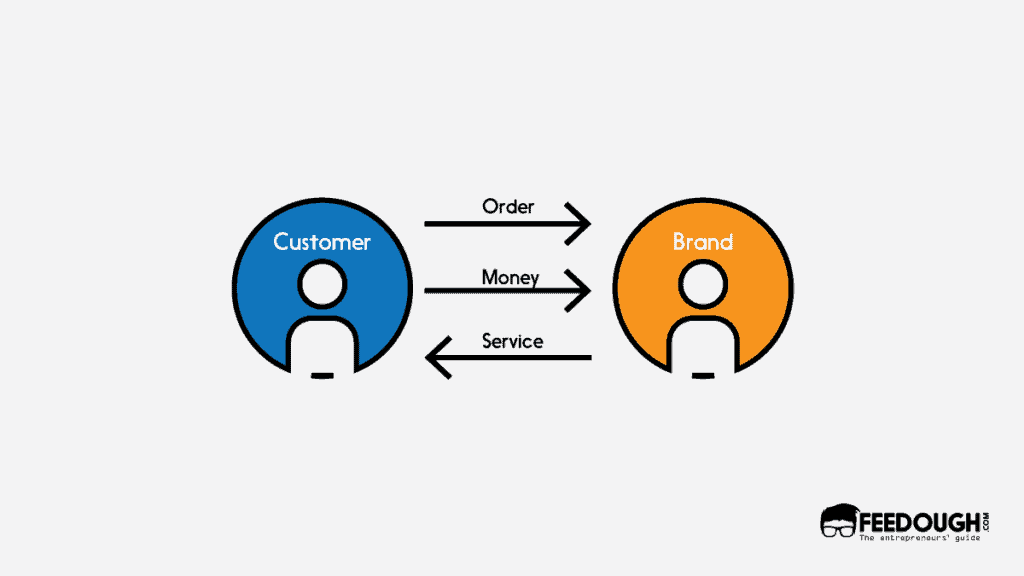
In the inventory led model, the hyperlocal business either produces its own offerings or buys them directly from brands and sellers and creates an inventory. This rules out the need to approach local stores after the order is made but bring in the element of managing the inventory and tracking customer demands for the business.
Aggregator Model
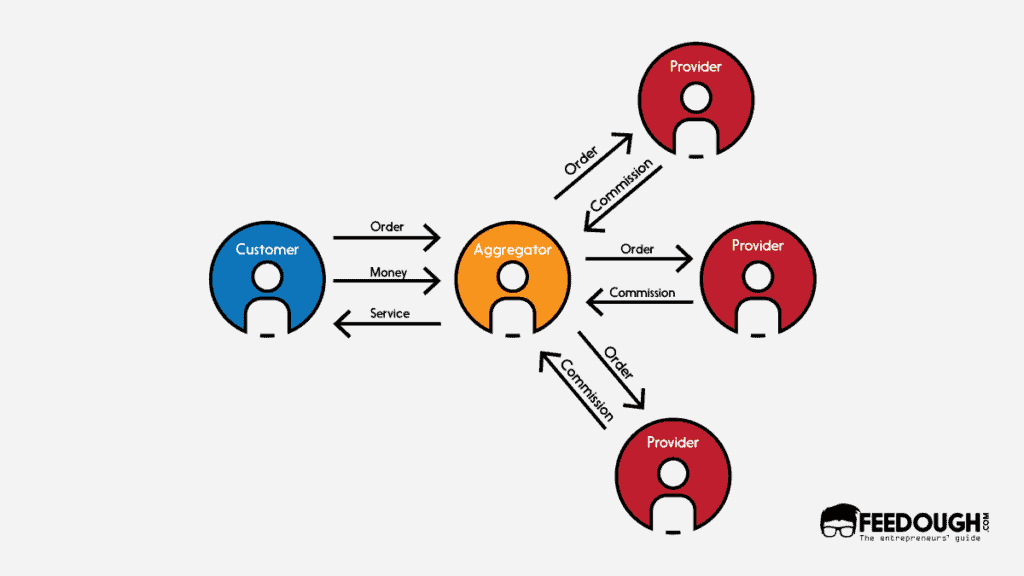
In the Aggregator or Zero inventory model, hyperlocal businesses act as a connecting bridge by linking the customers and retailers and ensuring last-mile connectivity and delivery to them. However, it provides the offerings under its own brand, no matter who it procures it from. Moreover, such an aggregator brand also makes sure to keep standardised prices and quality.
Consider the aggregator model as the Uber for hyperlocal offerings. The customer orders the offerings from the brand and the brand delivers it under its own name. However, the backend involves a partnership with an offering partner from where the brand procures the good and a delivery partner who delivers the offering.
Marketplace Model
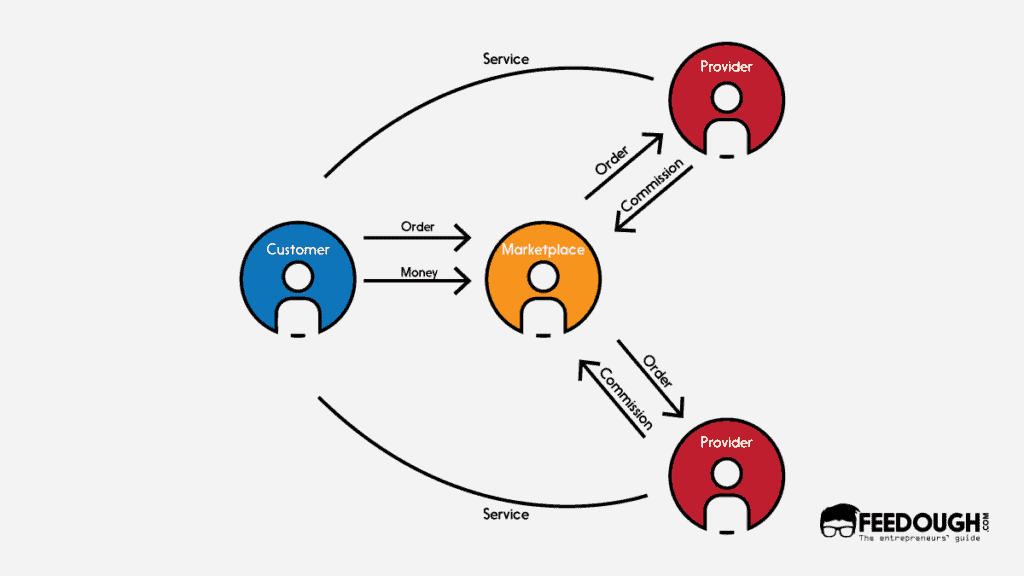
A hyperlocal marketplace model is one where the brand acts as a facilitator, connecting the customer with the retailers or sellers. That is, it provides a platform for several local retailers to sell similar items at prices they deem fit.
Unlike an aggregator, the marketplace model doesn’t demand standardised prices or quality. The brand only focuses on developing a discovery and ordering platform and sometimes help in delivery too.
Hybrid Model
It is a mix of the inventory, aggregate, or marketplace model and can be shaped depending on what suits the business the best. Businesses need to keep in mind the feasibility and viability of the system and the need and requirement of the customer segment they are targeting.
Target Customers Of A Hyperlocal Business
Hyperlocal platforms and applications usually target the tech-friendly prospects that belong to generation Z or millennials. Such customers value time over money and convenience over accessibility. They are known to be highly mobile-savvy and like using online apps for almost everything that is possible, ranging from ordering food and groceries or booking cabs to finding out about news and live events.
What Value Does A Hyperlocal Business Provide To The Customers?
Hyperlocal brands provide a level of convenience that is unmatched till now. Customers can order anything they want by just going online or downloading an app and placing an order. Customers prefer hyperlocal platforms because of the following reasons:
- Customers can place their order for items that are available on-demand or store pickup with the click of a button.
- It eliminates the need to visit a store to get the product. They can even order a number of items at once and split the bill at the end.
- Customers get more options to choose from. For example, they can pick from multiple stores and retailers.
- The process is transparent with real-time visibility of the transaction.
Key Partners Of A Hyperlocal Business
Since hyperlocal businesses operate mostly on marketplace and aggregator business models, their operating model revolves around two key partners –
- Offering partners: It constitutes the local store owners, manufacturers, wholesalers, or retailers who fulfil the offering demand of the customers. The hyperlocal business procures its goods from such partners.
- Delivery partners: It includes delivery personnel who work as partners for the hyperlocal platform and not employees. This saves money for the platform and give liberty to the partners to decide their own working hours.
Besides these two key partners, a hyperlocal brand also partners with several other partners that help it make its platform complete. They include –
- Map API Providers: Live order tracking is an essential feature of several hyperlocal platforms. To provide such a feature, hyperlocal businesses need to use map APIs provided by companies like Google. These map APIs help track the location of the delivery personnel and also show the progress of their order
- Payment Processors: The hyperlocal business needs to be equipped with a payment gateway or processor. Payment gateways help in keeping track of all the customer payments and ensure smooth order processing. Various payment gateways like Paypal, Stripe, etc. offer such services to hyperlocal businesses.
Key Resources Of A Hyperlocal Business
Broadly, hyperlocal platforms build their businesses capitalising on three key resources –
- Brand: The brand is the biggest resource they have. A hyperlocal business builds its brand by creating awareness, trust, and loyalty among its customers. The trust factor it creates helps it gain more orders and retain loyal customers who keep returning for their offerings.
- Technology platform: Hyperlocal businesses need a technology platform that manages the demand and supply, facilitates order-making and delivery, and tracks the location of customers. It must be capable of handling high volumes of traffic with minute-to-minute changes in consumer preferences
- Network: Network is a vital element to build an on-demand ecosystem. To make a hyperlocal platform work, a business has to focus on building a strong network of customers, offering partners, and delivery personnel.
What Channels Do Hyperlocal Businesses Use To Reach Customers?
The digital medium is the best way to reach out to a hyperlocal business’s customers. For example, Uber Eats has a website and mobile app for its users.
On all these platforms, customers can browse through information like menu cards, discounts, food festivals etc., reserve their order with the click of a button, pay online via net banking or cash on delivery, and track their order.
How Does A Hyperlocal Business Make Money?
Hyperlocal businesses make money in two ways –
- They charge a commission fee from the offering partners for every order they make.
- They charge a delivery fee from the customer for every order they deliver.
Some hyperlocal businesses also earn revenue by selling ad space on their platform. That is, they charge fees from the offering partners to feature them on the platform.
What Types Of Industries Can A Hyperlocal Platform Operate In?
Hyperlocal platforms can operate in any industry where there is a high demand for immediate, on-demand delivery.
They are good for various types of industries –
- Food delivery: The food and restaurant industry witnessed the advent of hyperlocal business models with the launch of online food aggregator platforms like Uber Eats, Swiggy, Postmates, etc.
- Grocery Delivery: Grocery delivery is a big market that several hyperlocal businesses have entered into. Instacart, Grofers, Bigbasket, and Amazon Now are some of the known names in the grocery business.
- Medical products delivery: Players like 1mg, Healthkart etc. are good examples of businesses operating as hyperlocal platforms for the sale of medical products ranging from medicines to equipment.
- Courier and Logistics: Players like Porter, Uber Connect offer hyperlocal courier and logistics services with the click of a button. They focus on delivering express or urgent couriers or parcels the same day via their delivery network.
- Home services: Home services is another area where hyperlocal platforms are set to disrupt the market. For example, players like Urban Company offer their service via their own network of service providers for home maintenance related issues like carpenter work, plumber work etc.
Bottom-Line?
In today’s world where it is so difficult to capture customer attention with the skyrocketing competition, businesses have started to realise the value of providing quality customer experiences and solving their problems.
Hyperlocal businesses are slowly but steadily growing in the global market. They provide a valuable solution to needs that could not be fulfilled by brick-and-mortar businesses earlier. It is an easy way for people to buy what they need at their doorstep without making any extra effort or travelling long distances.
The future of hyperlocal businesses is filled with vast opportunities. With the rise of the Internet, people are always online and want everything at their fingertips. So it is just a matter of time before hyperlocal business models replace our traditional ways to buy things completely.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on hyperlocal business model in the comments section.
An economics aficionado and a researcher at heart, Shrishti has also worked as a consultant to assist startups and NGOs in varied verticals. When not working, she is a passionate dancer and painter.








