“NFT of side-eyeing toddler meme fetches over $74,000 in cryptocurrency.” (The Washington Post)
“Somebody just paid $1.3 million for a picture of a rock” (CNBC)
“Twelve-year-old boy makes £290,000 from whale NFTs” (BBC)
These were some of the headlines on how NFTs are disrupting the market and surprising people every day. As it is, blockchain is a complex concept, and people have a hard time understanding the working and absurdities of it. Now NFTs, which are based on blockchain, have further confused tons of people while others are making huge profits by minting and selling them.
Many are still trying to figure out whether NFTs are a genuinely revolutionary technology that will forever reform various industries, just like cryptocurrencies did or if it’s merely a hoax that will gradually fade away.
But before jumping to these questions, it is important to understand the basics like what exactly is an NFT, how it works and most importantly, why are people ready to spend millions over assets that are available for free over the internet?
Read on to find out!
What Is An NFT?
NFTs, also known as Non-Fungible Tokens, are secure tokens or certificates that prove the ownership of unique items as a blockchain-based asset. In other words, NFTs work as tokens or certificates used to prove ownership of unique assets. Currently, they are usually used as collectables or investments as one can resell an NFT and earn profits based on its current value.
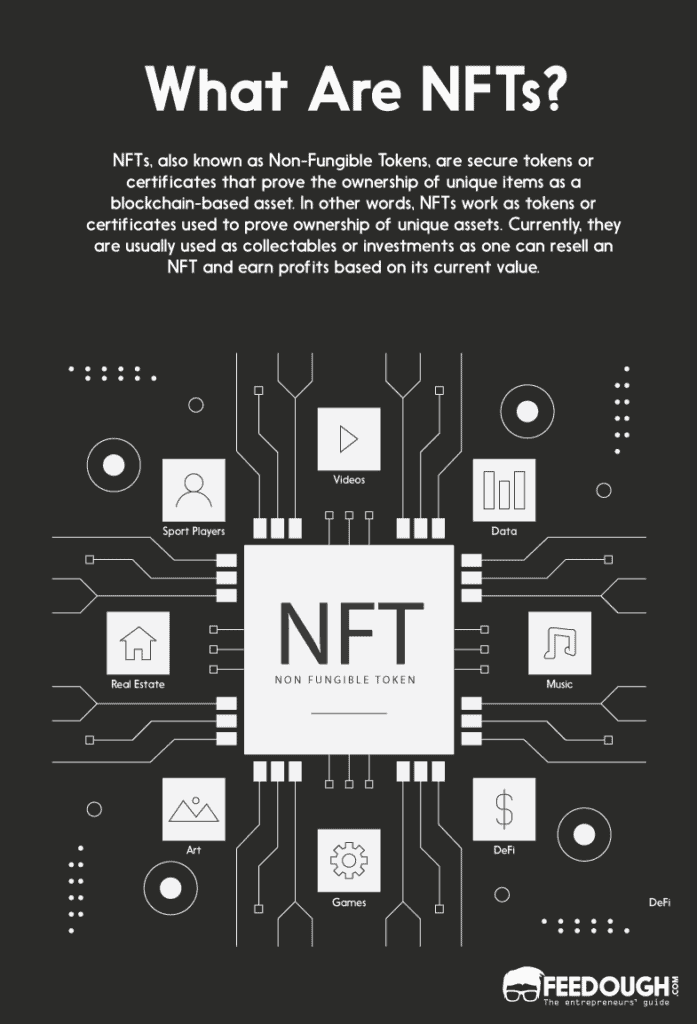
The following keywords further elaborate the meaning of NFTs:
Non-fungible
Fungible means something that can be exchanged. For example, one dollar can be exchanged for another as each dollar amounts to the same value. Likewise, one can easily exchange a 1 gram bar of gold for another 1 gram bar of gold as these are fungible assets. Non-fungible, on the other hand, means that the assets are one-of-a-kind and non-transferable. In other words, one NFT cannot be exchanged for another because each NFT represents a unique asset and thus, its value can differ based on different assets.
Blockchain-based
Blockchain is a decentralised digital ledger that stores information in a sequence of blocks and facilitates the process of recording transactions. Each block in a blockchain is connected to all the previous blocks as each block contains hash values of its previous blocks as well as of current transactions. Thus, if someone tries to change the information in one block, they will have to update all the blocks after it as the hash values change as soon as the data is tampered with. Furthermore, the system is transparent as all the blockchain participants have access to all the transactions. Also, the users need to reach a consensus in order to approve transactions in a blockchain. Thus it is nearly impossible to tamper with the data in a blockchain.
Therefore, a blockchain facilitates trust, security, efficiency as well as transparency among the participants.
NFTs are based on blockchain, making them extremely transparent and secure to transfer values over the internet. To be more precise, most NFTs are based on Ethereum, an open-source blockchain–based platform with its own cryptocurrency, Ether.
Ownership
Since NFTs are based on blockchain, they are secure, transparent and extremely easy to track, which is why they are used to prove ownership and verify the authenticity of unique assets. The ownership of an NFT is represented through a unique ID and metadata that no other NFT can duplicate.
How Do NFTs Work?
An NFT is minted from digital assets that can represent both digital and non-digital assets. For example, NFTs could represent:
- Digital art like GIFs, music, memes, videos, collectibles, in-game purchases, tweets, domain names etc.
- Non-digital items like deeds to a car, event tickets, legal documents, etc.
However, that is not it. Recently NFTs have been used to represent some of the most unexpected items. For example, not very long ago, Jack Dorsey, the CEO of Twitter, minted his first tweet as an NFT which was sold for just under $3 million!
One of the first use cases of NFTs was a game called CryptoKitties which allowed users to trade in virtual kittens. Recently, someone bought one of such kitties for $170,000 as an NFT.
How Is An NFT Created Or Minted?
The creation of an NFT is known as minting. There are various steps involved when an NFT is minted from scratch, including :
- Digitisation: The owner verifies the data and digitises it into an acceptable format
- Storage: The owner stores the raw data outside the blockchain. The owner is also allowed to store the data into the blockchain itself, but the operation consumes energy.
- Signing: The owner signs a transaction that includes the hash of the NFT. After that, the transaction is sent to a smart contract.
- Minting: After the smart contract is executed, the minting process begins, and a unique token for the NFT is generated.
- Confirmation: After the owner confirms the transaction, the minting process is completed and the NFT is linked to a blockchain that preserves and stores the data and its address.
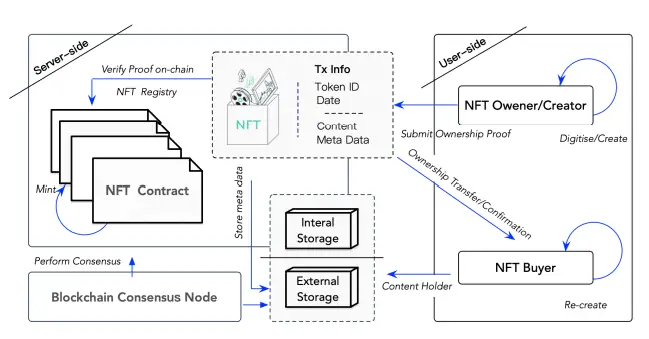
Smart Contracts
NFTs are secure and unique because they are minted using smart contracts, an essential part of any blockchain system. Think of a smart contract as the usual contract that proves the ownership of an asset or binds a person legally. Smart contracts simply constitute a bunch of code that is executed when some prerequisite conditions are met.
Whenever someone creates an NFT, the code (the smart contract) is executed, and the consequential information is stored in the block where the NFT is being managed. This is why NFTs are easily traceable as well as secure.
Proving Ownership Of An NFT
Although the digital assets which an NFT represents can be often duplicated or utilised by others, the NFT itself can only have a single owner. For example, recently, clips from a Logan Paul video were sold for up to $20,000. Now, this doesn’t mean that no one can watch, download or post that video, and it will be accessible to everyone on the internet like before. But the NFT for that video belongs to only one person who can further sell it or utilise it.
Since NFTs are based on the Ethereum blockchain, some of its unique properties are used to prove the ownership of an NFT and determine its value. One such property is cryptography. It is the process of developing a piece of information in a form so that it can only be understood by its intended recipient and no one else. The information transformed can only be enabled with a pair of keys called the public key and the private key. In other words, whenever an NFT is minted into a blockchain, each block is locked by a cryptographic hash that connects it to the previous hash. This hash can be decoded only with the help of the keys.
Moreover, NFTs are stored as tokens on the blockchain, usually the Ethereum blockchain and whenever one buys an NFT, they earn a right to transfer this token to their digital wallet. This token is what proves one’s ownership as well as the originality of the NFT.
Furthermore, a user’s private crypto key is the proof of ownership of the original digital copy, whereas the content creator’s public crypto key proves the originality of the asset.
Thus, if someone owns an NFT, they can easily prove their ownership with the combination of their private key as well as the creator’s public key.
What Are Nfts Used For?
NFTs have recently become really popular among artists and content creators as they allow them to successfully and securely monetise their art. NFTs allow artists to directly sell their art to consumers without relying on online platforms, galleries or auctions. Moreover, they can even program royalties into an NFT to get a certain percentage whenever their art is resold.
For example, recently, a video by Beeple was sold as an NFT for $6.6 million!
However, there are many other industries where NFTs are becoming increasingly popular including:
Gaming Industry
NFTs have seen a great boom in the gaming industry. They provide ownership records of items and promote economic marking in the ecosystem, thus benefiting developers and players.
- Players: while in a lot of existing games, players can purchase in-game items so as to make their experience more enriching, if the items are an NFT, players can resell these items after they are done with the game and may even earn some profit if the value of their NFT rises.
- Developers: publishers of NFT can earn royalties each time an item is resold in the marketplace.
Furthermore, NFTs can help in-game items outlive the game itself. For example, even if the game is no longer being developed, the items can still exist as an NFT, and thus they can have a value independent of the game.
There are a lot of games that are already utilising NFTs for various in-game purchases, thus increasing the scope of the game. For example, in a game called Decentraland, the players can buy digital land, which can later be resold and even be used as advertising space.
Virtual Events
With the help of their distinctive properties like uniqueness, ownership and liquidity, NFTs can be used to manage and control virtual events. Even though blockchain can be used for activities like funding, its applications are somewhat limited compared to NFTs.
One of the most common examples of the use of NFTs in managing virtual events is trading in the tickets market. In a traditional event, there is a centralised third party that the consumers are required to trust. Thus, there is a risk of numerous fraudulent activities such as selling counterfeit or invalid tickets. But an NFT-based ticket is unique and scarce, and thus, it cannot be resold or forfeited. Furthermore, the smart contract can be easily used to track the tickets sold and make the process transparent and trustworthy.
DeFi Or Decentralised Finance
Another popular and booming investment trend based on Ethereum blockchain is decentralised finance.
As evident by its name, DeFi is yet another disruptive technology that has made the financial world decentralised and transparent. It means that there is no central authority like central banks or the government controlling the printing or value of money.
One of the first and main applications of the DeFi system is bitcoin. Bitcoin allows one to easily hold money, control value and transfer it anywhere around the world. Furthermore, it is open to everyone, but no one can change the encoded rules, and thus the system is completely trustworthy.
Recently NFTs are being used in collaboration with decentralised finance so as to revolutionise the industry further. For example, NFTs have been used to :
- Solve the issue of collateralisation: Certain DeFi applications allow users to borrow money through collateral. Recently, NFTs tokens are being used as collateral to borrow money. This could eventually work with several things, thus expanding and tokenising the market.
- Execute fractional ownership: NFT developers are also allowed to create shares of their NFTs so as to allow traders to own a part of an asset without paying an enormous price for the whole NFT. Buyers can also sell these shares on DEXs (decentralised exchanges) in addition to NFT marketplaces.
How To Mint And Trade NFTs?
There is no such restriction as to who can create or ‘mint’ an NFT. Therefore, anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet can create work, create an NFT (called minting) and sell it on the marketplace. Moreover, one can even attach royalties with an NFT to earn a commission every time the NFT is resold. The only thing to keep in mind while creating an NFT is that one must be the original creator of the content.
However, as easy as it seems, minting an NFT is quite expensive. With every NFT sale, there comes numerous fees including a listing fee, a gas fee that is the price of energy for each transaction, a commission fee, and a commission as a transaction fee.
Several NFT marketplaces like Nifty Gateway, SuperRare, Foundation, OpenSea, Rarible, and Mintable allow one to buy and sell NFTs. These marketplaces are also known as NFT providers, and one can easily go to these marketplaces and buy or sell NFTs with cryptocurrencies in their digital wallets.
However, it is advised to have some knowledge about blockchain and cryptocurrencies before dealing in NFTs as these concepts can be a little complex and require at least some technical knowledge.
The Way Ahead
As is evident by several examples, NFTs have become very popular in a very short amount of time. They have successfully disrupted many industries, especially the creatives and the gaming industry. Artists, musicians, content creators, and others most benefited as they can now easily create and sell their work without any middlemen or auctions. They have even accelerated the applications of decentralised finance and disrupted the digital economic industry.
However, these are just initial applications as NFTs are a relatively new concept. NFTs still have a lot of potential to grow and further enter different industries. But, before that, there are certain hurdles, including certain copyright issues, accessibility, affordability, and the climate factor. The speed with which developers resolve these issues will determine whether NFTs can keep their momentum going or if it is merely a “hype”.
NFTs FAQs
Does the purchase of an NFT grant the copyright to the asset?
The ownership of an NFT does not by default grant the copyright to the underlying asset. This means that the owner of the NFT has no right to commercially exploit or use the asset as such.
However, this position can be varied through a smart contract which can be customised to specify the ownership rights to the assets. Alternatively, the NFT can also be accompanied by a sale contract or a copyright license specifying the proprietary rights including copyright.
How do NFTs impact the climate?
With the emergence of NFTs and their increasing popularity, there has also been an emerging concern that NFTs are not eco-friendly and negatively impact the climate. This is because NFTs are built on the blockchain technology which consumes an enormous amount of energy. It is estimated that each NFT transaction consumes the energy utilised by two American households in a day.
However, the Ethereum blockchain is continuously evolving and moving towards a less power hungry design. This speed of transformation of the Ethereum blockchain will play a huge role in the future of NFTs.
Can NFTs represent physical assets?
At present, NFTs are mostly used to represent digital assets as opposed to their physical counterparts. However, there is no restriction on the type of assets NFTs can represent and there are a lot of projects experimenting on the tokenisation of real-estate or unique fashion items.
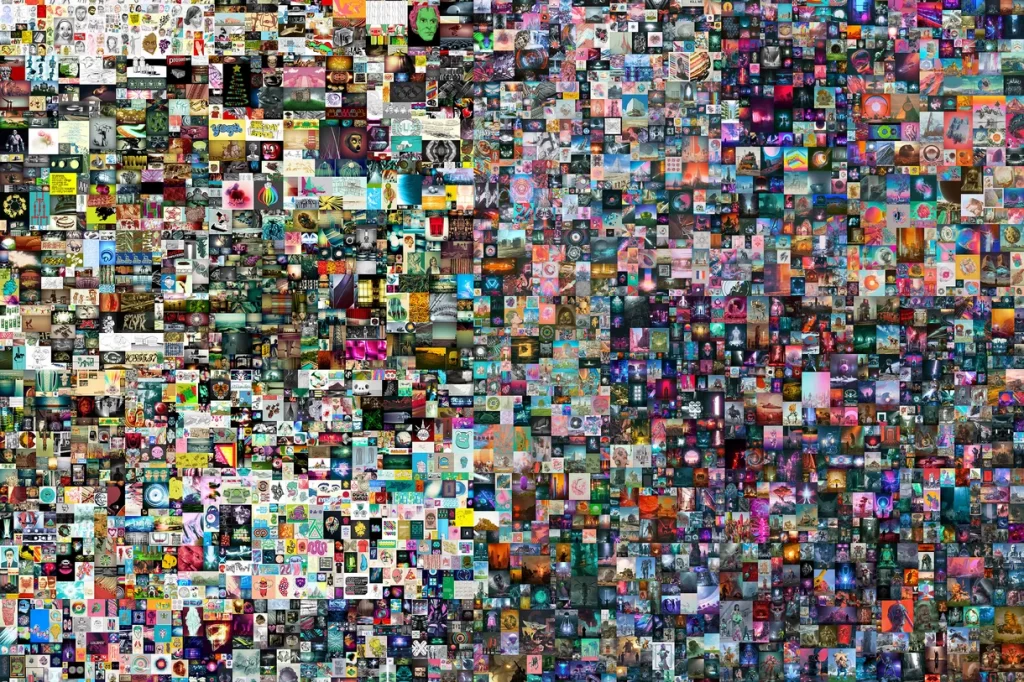
What is the most expensive NFT ever sold?
The most expensive NFT ever sold is an artwork created by Mike Beeple Winkelmann called “Everdays: The First 5000 Days”. The artwork representing a collage of Beeple’s first 5000 artworks was sold for $69.3 million.

Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of our article on the Non-fungible tokens (NFT) in the comments section.
An enthusiastic human being with determination and zeal to explore new ventures. Tanya is an entrepreneurial spirit searching for changes and learning to exploit them as opportunities and impacting people for good.




![What Is A Cryptoasset? Types Of Cryptoassets [Ultimate Guide] cryptoassets](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/cryptoassets-02.webp)


