You must have heard people talking about some confusing words like blockchain, decentralisation, cryptocurrency, cryptography and many more. Well, these words are not so random anymore. They are the pillars of the future of finance. For instance, blockchain has completely revolutionised the financial sector by introducing decentralisation as well as security and transparency.
But when did it all begin? What was the starting point of blockchain? Who invented it? The answer to all these questions is Bitcoin. Bitcoin marked the beginning of the decentralised financial system when a pseudonymous user named Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin in 2009. But, Bitcoin isn’t a blockchain. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency based on a blockchain.
Confused?
Let’s decode all these terms one by one.
What Is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a decentralised, transparent and peer-to-peer based digital currency secured by cryptography that operates on blockchain technology.
In simple terms, it is a digital currency in which encryption techniques are used to regulate the generation of currency units and verify the transfer of funds, operating independently of a central bank.
Precisely, cryptocurrency is digital money that eliminates an intermediary or a central authority. In fact, the main idea behind the concept of cryptocurrencies and blockchain was to introduce decentralisation in the financial ecosystem.
Decentralisation means that no central authority, like the government or central banks, regulates the operation of cryptocurrencies. This makes all cryptocurrencies censorship-resistant and immune to any kind of third-party manipulation.
It all began in 2009 when a pseudonymous person (or group) named Satoshi Nakamoto came up with Bitcoin. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency ever, and this is when the concept of blockchain and cryptocurrencies came to life. Blockchain is a decentralised digital ledger that stores and records transactions in a sequence of blocks that are chained together.
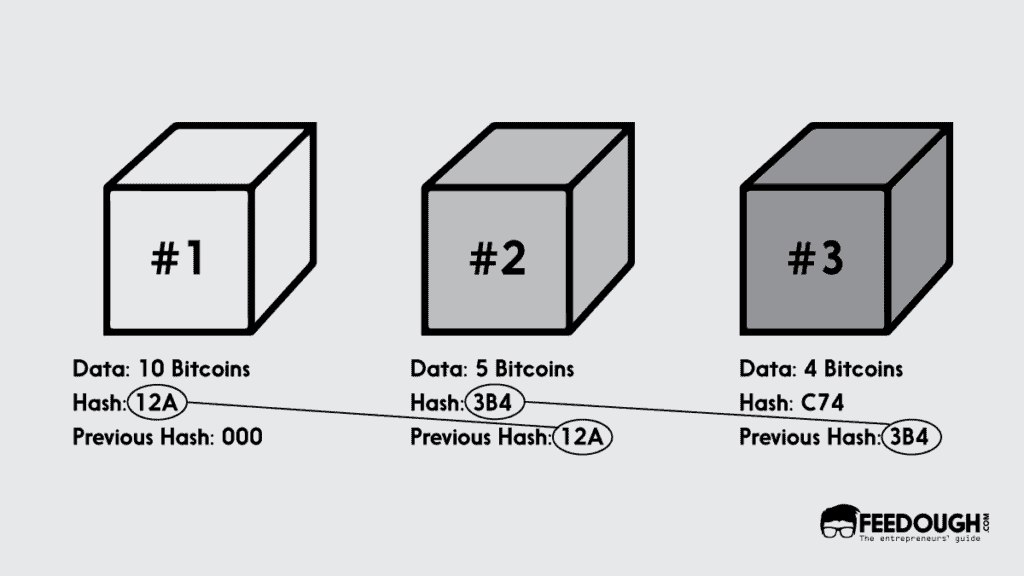
Each block is connected to its previous block in a blockchain as each block contains the hash values of current transactions and the transactions stored in the last block.
Every new transaction after verification gets added to a new block which is then linked to all other blocks making up the chain. The whole process makes it almost impossible to change or alter any information that has already been recorded.
Consider blockchain to be similar to the game of Jenga. Every block is a Jenga piece that can be moved or played with, but once you tamper with a piece from the bottom, it makes it harder for the following blocks to sustain.
In this way, blockchain technology is built in such a manner that as more records are added to it, it gets increasingly difficult to make changes as there would be a lot of records that would need to be altered.
If anyone tries to change the information in one block, they will have to update all the blocks after it because the hash values change as soon as the data is edited. So, each block in a blockchain is permanent, and all the users can see every transaction in a public blockchain along with its time-stamp.
This makes blockchain technology secure and incorruptible over time.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
The concept of cryptocurrencies works on three pillars: blockchain, cryptography and crypto mining. Let’s take a look at these terms one by one.
Cryptography
Cryptocurrency is a portmanteau of two words – crypto and currency. The word crypto comes from cryptography, which is the main concept behind the working of cryptocurrencies.
Cryptography is a method of securing information so that only the intended recipient can understand it. Cryptocurrencies use two keys called the private key and the public key.
The public key can be considered your bank account number, which can be shared with others to enable crypto transfers to your wallet.
The private key can be thought of as a card pin that shouldn’t be shared with anyone. The private key is used to secure and access one’s crypto holdings and sign transactions.
What happens behind the scenes is that an algorithm is used to encrypt the user information. This algorithm takes the public key as input to encrypt the information and requires the private key to decrypt the same information. That is why the private key must be kept secret so that only the intended user can decode the required information.
Crypto Mining
One of the most basic questions that come to mind while understanding cryptocurrency and blockchain is, who enters new blocks to a blockchain? Or, why can’t one reverse or change a blockchain transaction? The answer to these questions is crypto mining.
Crypto mining is a phenomenon that helps in maintaining the blockchain by attaching more transactions in the blockchain and rewarding the miner with cryptocurrencies for the same. This process encourages miners to maintain the blockchain by minting more and more cryptocurrencies and allowing new coins into circulation.
Crypto mining is a two-fold process. First, the miner verifies the transaction in question to ensure that everything is in order and the sender has authorised the transaction using their private key. The second step involves creating a new block in the blockchain and attaching it with the previous block.
There are various ways of mining cryptocurrencies. Two of the most popular ways are:
- Proof of work: in the proof of work system, the miner needs to solve a computational mathematical equation or a cryptographic puzzle. Whoever first solves this puzzle gets the reward for mining the cryptocurrency. What happens behind the scenes is that miners try to come up with a hash less than or equal to the target hash. This is the hash that links the current block with the previous block in the blockchain.
- Proof of stake: instead of getting the miners to compete with each other, proof of stake works on a consensus-based algorithm in which a node is randomly chosen to validate the data in the next block. But the process is not completely random. First, a node is required to deposit a certain amount (or stake) into the network. The higher the amount deposited, the higher are the chances of a node becoming a validator. Then the validator verifies all the transactions and then adds them to the blockchain. As a reward, the validator receives the fees associated with each transaction.
Although proof of work and proof of stake are the most popular ways of crypto mining, there are tons of other ways like proof of coverage or proof of space. As new blockchains come into existence, the developers try to find different ways to mine cryptocurrency and maintain the blockchain to improve energy and time consumption.
Key Terms Related To Cryptocurrencies
Some of the essential terms related to crypto include:
- Crypto assets: this is a blanket term that refers to all the assets that operate on a public ledger and utilise cryptography. The difference between cryptoassets and cryptocurrency is that cryptoassets are not limited to just cryptocurrencies. They also include various utility tokens, platform tokens, and tokenised securities. For example, Bitcoin BTC is a cryptocurrency. On the other hand, utility tokens like LOOM that provide access to a blockchain-based service are considered cryptoassets.
- Cryptocurrency: this refers to a form of digital or virtual currency that is decentralised and uses cryptography to secure the transactions and control the creation of new units. All cryptocurrencies are crypto assets, but not all crypto assets are cryptocurrencies. This is because some crypto assets like LINK has a different use case than to challenge the traditional financial system.
- Crypto tokens: this category includes assets like fungible tokens, non-fungible tokens (or NFTs) and DeFi tokens. Crypto tokens are crypto assets that are not native to any particular blockchain. Although Ethereum is the most utilised blockchain to mint tokens, several other blockchains support them.
- Cryptocurrency miner or mining rig: these are computers or servers that are specially designed to solve complex mathematical problems in order to generate cryptocurrency.
- Cryptocurrency wallet: this refers to a digital wallet that is used for storing and transferring decentralized cryptocurrencies from one user to another. Using these wallets, users can also send and receive coins or tokens.
- Cryptocurrency Exchange: this is a platform where cryptocurrencies can be bought, traded or sold against fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies. Most of these exchanges also offer crypto wallets that allow users to hold their digital currencies securely.
Types Of Cryptocurrency
There are various types of cryptocurrency based on their use cases including:
- Payment cryptocurrencies: These cryptocurrencies are designed to make payment solutions faster and more secure by replacing the traditional banking systems. For example, currencies like Bitcoin or DAI are designed to serve as an alternative to traditional cash. They are generally pegged to traditional assets to provide price exposure and stability to established values while giving the benefits of transparency and decentralisation.
- Infrastructure cryptocurrencies: These cryptocurrencies are used to maintain and use applications of a particular blockchain. For example, Ether is an infrastructure cryptocurrency as users are required to purchase it to use any decentralised application running on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Financial cryptocurrencies: The main application of financial cryptocurrency is to manage or exchange other crypto assets. For example, they may be used to help users trade on exchanges, crowdfund money, lend or market cryptocurrency and speculate on the outcome of certain events. Examples of such cryptocurrencies include Compound, Balancer, Curve or Gnosis.
- Service cryptocurrencies: These cryptocurrencies are used to manage and record data from different industries and link them to blockchain. For example, a cryptocurrency called Dentacoin provides various services related to the healthcare industry. Other examples of service cryptocurrencies include Chainlink, Filecoin, Orchid, etc.
- Media and entertainment cryptocurrencies: Media and entertainment cryptocurrencies are used to reward users for content or games and are even utilised in various decentralised applications that utilise virtual reality to operate.
How To Invest In Cryptocurrency?
Investing in cryptocurrency is becoming increasingly popular as many people have earned huge profits through buying and selling cryptocurrency using speculation.
There are two ways through which a user can invest in cryptocurrencies. They can either use a crypto brokerage firm or a crypto exchange:
Cryptocurrency Brokerage
A crypto brokerage is a firm or an individual that acts as a mediator and facilitates the buying and selling for the user. This is a good option for someone who is just a beginner in crypto trading and wants to explore and study the market.
To trade using a crypto brokerage, the user must sign up to make an account with any brokerage of his/her choice like Coinbase, Gemini and eToro. After that, the user can fund the account and then choose a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin or Ethereum to begin investing.
Cryptocurrency Exchange
A crypto exchange allows a user to directly trade with other buyers and sellers by eliminating the intermediary. Using a crypto exchange, the user can trade cryptocurrencies for other decentralised and digital currencies or fiat currencies based on current market prices. Crypto exchanges are a perfect platform for advanced users and traders who trade in crypto through speculations. Some examples of popular crypto exchanges include Binance, Kraken or Coinbase.
Why Invest In Crypto?
There are quite a few advantages that make it attractive for investors as well as for traders. While trading and investing are not the only two applications of cryptocurrency, they are so far the most popular ones. Many people use speculation as a technique to invest money in crypto and make huge profits. Some of the major benefits of investing in cryptocurrency are:
- Low transaction costs: Cryptocurrencies work on a decentralised blockchain system. This means that there are no intermediaries such as banks or brokers and hence there are no additional transaction costs except for the blockchain network’s fees. Furthermore, there are no requirements for any kind of paperwork or identity proof. The whole process is smooth, easy and extremely fast.
- Globalised access: Unlike with banks or centralised authorities, there are no restrictions as to who can use cryptocurrencies. Anyone with an internet connection and funds to transfer can invest and trade in crypto. However, there are some countries that ban the use of crypto for their citizens but blockchain or crypto as a system doesn’t restrict access to any user whatsoever.
- Immutable transactions: Unlike in traditional financial systems, the transactions made through crypto coins are immutable. This means that once a transaction is added to a blockchain, it cannot be reversed or tampered with at all. Thus, the records of all the transactions are accessible by all the members forever. Also, there is no way for anyone to reverse a crypto transaction once it is made.
- Secure network: Cryptocurrency is based on an extremely secure technique called cryptography. While traditional currencies could be stolen or destroyed, it is challenging to steal crypto since one needs the public as well as the private key of a user to access the crypto stored in a wallet. Although there have been reports of hackers figuring out users’ private key and hacking into their wallets, the process is extremely difficult, making crypto much more secure than fiat currencies.
- Self-controlled and self-managed: Since cryptocurrency completely eliminates the need for an intermediary, it is potentially free from the whims and control of a third party. For example, banks have the authority to close your accounts while the government has the authority to print money or lower government expenditure or increase and decrease interest rates as per their discretion. But, with cryptocurrency, the value of various coins are decided solely on the basis of demand and supply. No one has any authority over anyone’s funds and everyone is a part of the community.
Cryptocurrency Risks And Challenges
While cryptocurrency and blockchain have many advantages and use-cases, users also face certain challenges and risks while using crypto. Most of the risks stem from the fact that cryptocurrencies are not regulated, thus there is no one to look after the users and their security.
Some major risks and challenges include:
- Regulatory and compliance risks: In a cryptocurrency system, anyone can create multiple accounts while being completely anonymous. There are no regulatory rules or guidelines which the users are supposed to follow and this creates potential risks of illegitimate activities such as money laundering or drug trafficking. This is the reason why some countries like China have banned the use of cryptocurrencies.
- Trading costs and illiquidity: When compared with the traditional centralised currencies, cryptocurrencies are generally less liquid and more volatile. This is because the supply and value of cryptocurrencies are only determined by the value placed on them by the users through their transactions. Furthermore, some crypto exchanges continuously manipulate prices by trading against their users. This further makes the cryptocurrencies illiquid and increases trading costs.
- Cyber threats: The biggest advantage of cryptocurrencies is that they do not rely on any traditional financial institution. This lack of regulation is what imposes the threat of cyber attacks. Furthermore, as cryptocurrencies are completely based on code, there is a potential risk of hackers breaking into crypto exchanges and crypto-wallets. The cyber threats are extremely serious and may lead to huge losses with little recovery potential at the user’s end. For example, suppose somehow a hacker gets access to a user’s private key. In that case, they can easily gain access to the user’s wallet and even impersonate all of the user’s transactions and transfers.
- Energy costs: Another challenge in the use of cryptocurrencies is the energy costs while mining crypto coins. The proof of work required while mining cryptocurrencies consumes a lot of energy depending on the system’s hardware performance. Since almost all the cryptocurrencies require proof of work, this also impacts the environment as more electricity means increased carbon emission and thus increased global warming.
FAQs on Cryptocurrencies
How many cryptocurrencies are there?
As of 2021, more than 6,800 cryptocurrencies have been identified. Some of the most popular ones include Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Cardano, PolkaDot, Stellar, etc.
Is cryptocurrency the same as digital currency?
No, a digital currency is not the same as a cryptocurrency. Digital currency is simply the electronic form of fiat currency issued by the central authority. Their use has recently increased so as to achieve contactless transactions. But, these currencies are still centralised, stable and not at all transparent.
Does cryptocurrency have an infinite supply?
This statement is partially true. First of all, not all cryptocurrencies have an infinite supply. For example, Bitcoin has a limited supply of 21 million coins. And of these almost 90% of coins have already been mined. Thus, after all 21 million coins are mined, the miners will receive their rewards through fees of transactions.
Now, some crypto coins such as Ethereum have an infinite supply. But, these could lead to huge inflation. So, the developers have tackled this issue by fixing the number of coins to be generated every year. Thus, the supply is unlimited only in the long run. In the short run, for example in a year, only 18 million Ether coins can be mined.
How are cryptocurrencies assigned value?
The answer to this question is simple. Cryptocurrencies have value because people become them to have value. Just like other currencies, crypto does not have an inherent or intrinsic value. For instance, take the example of fiat currencies. Suppose the government or the central authority of any country declares that a certain currency no longer holds any value. In that case, people will stop using that currency and it will immediately lose all value. The same is the case with cryptocurrencies. The users themselves decide the value of crypto coins by believing that they can be used as a currency and store value. Thus, the value of almost all the crypto coins is decided by the forces of demand and supply.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on what is cryptocurrency? in the comments section.
An enthusiastic human being with determination and zeal to explore new ventures. Tanya is an entrepreneurial spirit searching for changes and learning to exploit them as opportunities and impacting people for good.



![What Is A Cryptoasset? Types Of Cryptoassets [Ultimate Guide] cryptoassets](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/cryptoassets-02.webp)




