One of the most important functions of the Human Resources Division of any company today is Talent Management. Talent management plays an important role in the business strategy since it manages one of the company’s most important assets—its people.
Talent management starts with understanding the jobs that need to be filled and the human traits and competencies needed for these jobs effectively. Job Analysis precisely determines the duties of the company’s positions and the characteristics of the people to hire them.
An integral product of Job Analysis is the Job Description.
What Is A Job Description?
A job description is a written statement of what an employee actually does, how he or she does it, and the job’s working conditions. This information is then used to write a Job Specification—a part of the Job Description—that lists the knowledge, abilities, and skills required to perform the job satisfactorily.
An entrepreneur can use a good job description not only as a valuable aid in the job-recruiting process but also as an outline for reporting relationships and working conditions. It can be used for:
- Performance Management
- Training and Employee Development
- Compensation
- Recognition and Rewards
- Maintaining Discipline
Elements Of Job Description
What elements should a Job Description contain? What should the format of a Job Description be?
Here is the answer:
Job Identification
It contains the job title, specifying the name of the job, such as inventory control clerk, management trainee, supervisor, etc. It might also contain the location in terms of its facility/division and department or the supervisor’s name and details. In cases where a category is used for defining the job, such a category is clearly stated.
Job Summary
A job summary contains the essence of the job and includes only its major functions and activities. For a supervisor, the job summary could be: ” The mailroom supervisor receives, sorts, and delivers all incoming mail property.”
Responsibilities, Duties, And Authority Of The Incumbent
This essentially forms the heart of the Job Description. It should present a list of the job’s significant responsibilities and duties. Example – For a sales role, the responsibilities would look like “achieve quantitative sales goal” and “determine sales priorities and fulfil targets”. This part might also specify the jobholder’s authority limits. This is essential because it specifies the limits within which the employee has to function and also gives him/her an idea of the kind of stakes involved. For example – a job holder might have the power to approve purchases up to Rs 10000, take leaves without informing up to 2 times a month, or hire a sales assistant after completion of specific targets, etc.
When a Job Description is written for the disabled, care has to be taken to ensure that the person has the required skills and expertise to perform the job. Factors to consider are:
- Whether the position exists to perform that function.
- The number of other employees available to perform the function.
- The degree of expertise or skill required to perform the function.
Standards Of Performance And Working Conditions
This section lists the standards the company expects the employee to achieve for each job description’s main duties and responsibilities. One way to set standards is to finish the statement, “I will be delighted with your work when….”. This sentence and the like should result in a usable set of performance standards that can be easily identified and measured. Example –
Duty: Accurately posting Accounts Payable
- Post all invoices within the same working day.
- Allowed to commit no more than five posting errors each month.
- Route all the invoices to the proper department managers for approval by the following day.
The job description may also list the job’s working conditions, such as the noise level during work hours, any specific hazardous conditions, exposure to heat, etc.
Job Specification
Also known as employee specifications, this section states the human traits, qualifications, and experience required to perform the job. It shows what kind of person to recruit and on what qualities should the person be tested. Elements of job specifications are –
- Qualification
- Experience
- Training
- Skills
- Responsibilities
- Emotional Characteristics
- Sensory Demands
Company Profile
Even though not visible at first glance, the company profile is still a very important element of a job description. It gives job applicants a glimpse of the company’s achievements, culture, and other important information. The profile also includes links to social media profiles, company mentions, and testimonials, which may help the job applicant learn more about the company.
How To Write A Good Job Description?
Writing a job description is easy. Thousands of people do that every minute. But how do you write a job description that stands out? How do you improve your job response and get more qualified applicants to apply for your job listing?
Here’s the secret sauce –
Write A Crisp Job Title
According to a study, words like “ninja,” “badass”, “unicorn”, and “rockstar” are significant deterrents for women job seekers. Also, avoid using superlatives like brilliant, excellent, etc., as they give an impression of unrealistic goals and result in fewer job applications.
Write a job title that explains –
- The job responsibilities. For example, job titles that include a suffix or prefix like manager, chief, supervisor, etc.
- What the person does on the job. For example, housekeeper, chef, social media manager, etc.
- The job responsibilities and the job level. For example, chief accountant, head supervisor, electrical superintendent, etc.
Keep your job title simple, crisp, and not misleading. For a Call Center Agent, write that you’re looking for a ‘Call Center Agent’, not a ‘Sales & Marketing Executive’. Such disingenuous job titles attract the wrong people, increase your workload, and you may even miss out on qualified candidates.
Don’t Overexplain
When writing a job description, be professional and relatable. Most candidates skim job descriptions, so try avoiding jargon and long paragraphs. Be to the point. You can always explain the intricacies in the later stages.
Focus On The Structure
Your job description should be visually appealing. Divide it into sections, write small paragraphs, and use bullet points and formatting tools to help skimmers find the details they are looking for.
Write A Clear Job Specification
You should know the difference between a job description and a job specification. While job specification is a part of a job description, it has a different role altogether.
The job specification states what qualifications, experience, traits, etc., the company is looking for in an ideal job candidate.
Writing a Job Specification for trained people is relatively simple, with the focus on previous job experience, quality of training, and other hard skills. The problem is more complex when you’re writing a job specification for untrained people. Here, the focus is on qualities such as physical traits, personality, interests, or sensory skills that show the person’s potential for performing the job efficiently.
Using your own judgement to prepare a job specification would include the use of generic and universal traits that are desired from every employee. These would include soft skills like industriousness, ability to learn, taking initiative, displaying high integrity, etc.
Basing job specifications on statistical analysis rather than only judgement is the more desired and difficult approach. The aim here is to statistically determine the relationship between some human traits and some criteria of job effectiveness, such as performance. This procedure has the following steps:
- Analyse the job and decide how to measure performance.
- Select personal traits that you believe should predict performance.
- Test candidates for these traits.
- Measure these candidate’s subsequent job performance.
- Statistically analyse the relationship between human trait and job performance.
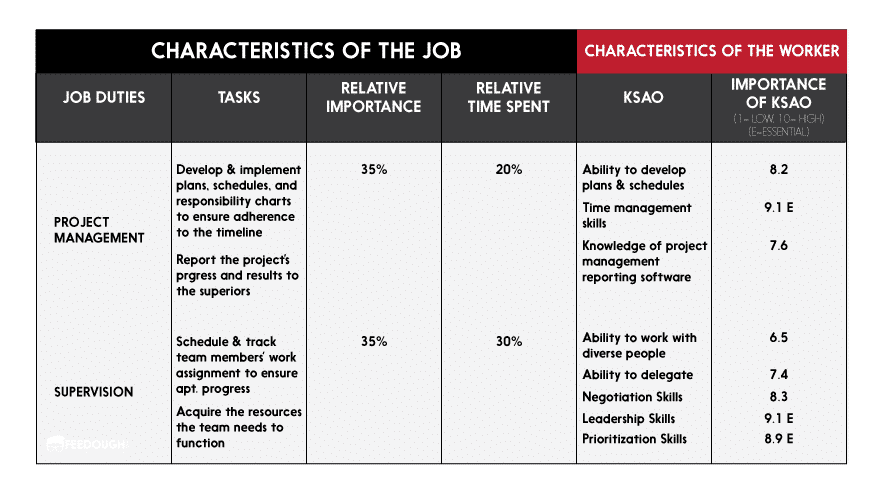
Another method that can be used is The Job Requirements Matrix.
A typical matrix uses five columns in the following manner:
- Column 1: Each of the job’s four or five main duties.
- Column 2: The task statements for the main tasks associated with each job duty.
- Column 3: The relative importance of each job duty
- Column 4: The time spent on each job duty
- Column 5: The knowledge, skills, ability and other human characteristics (KSAO) related to the main job duty.
- Column 6: Importance of KSAO
Focus On Other TouchPoints As Well
Sell Your Company!
Look out for touchpoints other than the job listing portal and ensure they are in synergy. These include company review websites like Glassdoor, Google My Business; your own website, your careers/work with us page, social media profiles, etc. A good practice is to mention the positive reviews and give these links in the job description.
Sell Your Job
Your job description should also contain triggers and compelling benefits that make candidates apply for your job instead of others in the listing. It should also include compelling reasons for candidates to leave their current jobs for good.
Don’t Use These Strategies
Job descriptions should be an offer to invite everyone who is capable to apply for the job. Make sure you stay away from these practices –
Discrimination: Even an unconscious bias against any specific sex, gender, race, caste, etc., will cost you a lot of good candidates.
Unrealistic Requirements: Identify what’s required and what can be learned during the job. Job specifications should only have minimum requirements. Based on the other stages, you can select the perfect candidate.
Negativity: A job description aims to get as many job applications as possible. Try to be as positive as you can. Don’t sound rude or negative. Instead of framing the sentence like this – “don’t apply if you don’t have at least four years of experience”, frame your sentences in this manner – “This is a senior-level job. Preference will be given to candidates having more than four years of experience.”
A marketing professional, enthusiastic about connecting with new people and exchanging ideas. An avid traveler open to exploring new cultures and experiences








