A goal without planning is just a dream. You need a ‘start to finish’ plan in order to ensure effective use of resources and better results. For marketers, imagining a buyer’s journey is an integral part of planning an effective marketing strategy, and there’s a perfect tool for the same: the marketing funnel.
Like an actual funnel, marketing funnels represent a buyer’s journey from being aware of an offering to becoming its loyal customer. It’s a step-by-step process that narrows down your target audience as they move further down the funnel, culminating in conversions and sales.
But before we move towards the functioning of a marketing funnel, let’s first understand what it is.
What Is A Marketing Funnel?
A marketing funnel is the visualisation of the buyer’s journey from the point when they first learn about the product or service to when they eventually become a customer.
It’s a step-by-step process that businesses use to nurture prospects and turn them into paying customers.
In simple words, a marketing funnel is a process that takes a customer from awareness to purchase.
Sounds puzzling? Let’s ease it further.
Imagine an actual funnel.
You pour water in the wide opening at the top, and it eventually comes out of a small hole at the bottom, right?
Now, think of your marketing funnel as that actual funnel.
- The top of your funnel is where your target customers get to know you.
- The middle is where they learn more about your product or service.
- And the bottom is where they finally make a purchase.
The main purpose of a marketing funnel is to move your target customers from the top of the funnel (TOFU) all the way down to the bottom so they eventually become paying customers.
Marketing Funnel Stages
Most marketers categorise the marketing funnel into four main stages (AIDA model).
- Awareness: Where the target audience becomes aware of the product or service.
- Interest: When they start showing interest in what the brand has to offer.
- Desire: When they start wanting the product or service.
- Action: When they finally take action and make a purchase.
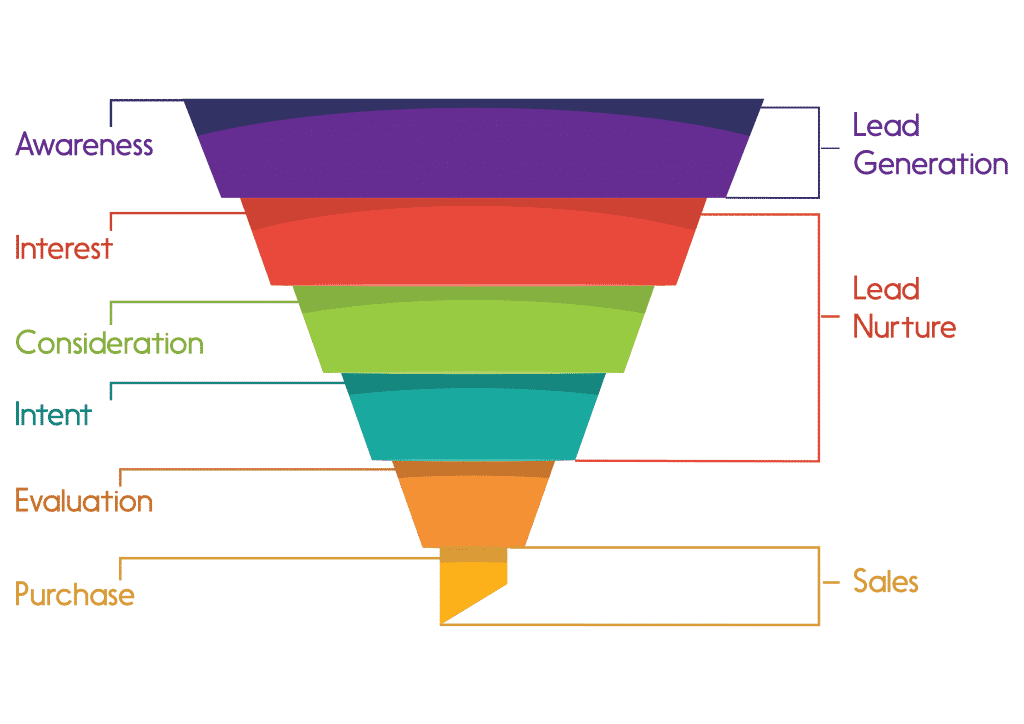
However, with the advent of the internet, the marketing funnel has become more complex with the addition of new stages. The modern marketing funnel today has six levels:
- Awareness
- Interest
- Consideration
- Intent
- Evaluation
- Purchase
Awareness
From a customer perspective, the awareness stage is all about getting to know your brand for the first time.
They might’ve seen a Facebook ad, read an article that mentioned your product, or heard someone talking about your company.
At this stage, customers are still trying to figure out what they need and whether your product is the right fit for them.
From a marketing standpoint, the awareness stage is all about getting your name out there and generating interest in your product. People at this stage of the funnel are named prospects and marketers try to convert them into leads by sharing relevant content.
Marketers focus on the following objectives during the awareness stage:
- Generate brand awareness
- Increase reach
- Build credibility and reputation
They achieve the same using the following techniques:
- Content marketing: This involves creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content in the form of blog posts, infographics, ebooks, etc., to attract and get the attention of your target audience.
- Search engine optimisation: This is the process of optimising your website to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) for certain keywords, which, in turn, will generate more traffic to your site. SEO is complemented by content marketing.
- Social media marketing: This involves using social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Pinterest to build relationships with potential and current customers. Marketers post relevant content that has the potential to go viral and get shared by a large number of people.
- Paid advertising: These are advertisements that appear on search engines, social media platforms, and third-party websites in the form of images, videos, or text. Marketers can use paid advertising to target relevant audiences with laser precision.
- Public relations: Public relations is the process of managing the spread of information between an individual or an organisation and the public. Public relations activities can include organising press conferences, conducting interviews, and writing press releases to generate positive publicity and spread awareness about a brand.
- Referral marketing: Referral marketing is a form of marketing that relies on word-of-mouth from satisfied customers to generate new leads. Referral marketing can be done through online platforms such as social media and review websites, or offline through personal recommendations. Referrers help the brand reach new customers in return for a reward, such as a discount or free product.
- CPA marketing: CPA marketing, or cost-per-action marketing, is a form of affiliate marketing where you pay a commission for each action taken by a customer. This could be a sale, sign-up, or any other desired action. CPA marketing is a popular model for lead generation as the task to inform the customer about the product or service is already completed by the referrer, so what you get is already a lead deep down in your funnel.
For example, a person with yellow teeth may have just realised that they’re not happy with their smile. They start to do some research using keywords like “best teeth whitening products” or “how to get whiter teeth.” He may also talk to friends or family members about their experiences with different teeth whitening products.
This is the touchpoint where your brand needs to be visible.
Interest
At this stage, the prospects know that the brand exists and want to learn more about what it offers. The marketing funnel begins to narrow here as the prospect starts to compare different options and make a decision.
In marketing terms, these prospects have already converted into leads, and the goal now is to turn them into customers. But there’s a long way to go before that can happen.
This stage involves nurturing this early-stage lead by answering its comparison questions and addressing any objections it has about the brand.
For example, once aware of the available options for teeth whitening products, a customer may be interested in three to four, depending on their needs. If the offering lies among these, the marketing team’s job is to ensure that their product is the one that stands out. It does the same by understanding what the customer searches for next. Some examples include “XYZ brand pricing” or “XYZ brand features”.
During the interest phase, the customer just needs more information regarding whether the product has all the features they’re looking for and whether it’ll –
- Help them get the job done
- Solve the problems preventing them from getting the job done
- Provide them gains related to the job getting done
You need to generate content that is both informative and persuasive, addressing the customer’s objections while also furthering their interest in the product.
Consideration
Getting favourable answers during the interest phase paves the way for customers to consider your product as something they can buy.
In simple terms, now the customer has a soft corner for your product, but they may need more information and persuasion to make the purchase decision.
The consideration stage is where people start to compare your product with other similar offerings in the market. They weigh the pros and cons and look for what others are saying about your product through reviews and testimonials, trying to figure out if it’s worth their money.
You’d need strong social proof and some more content in the form of third-party blog posts and videos to push them further down your funnel.
- Affiliate marketing works best during the consideration phase. Review posts by known bloggers and vloggers, or even better, personal recommendations from people they trust can do wonders for your product.
- A dedicated feature information page on your website or brochure for every feature your product or service offers can also be very helpful in this phase.
Intent
An intent stage is when the prospective customer does some specified activity after the consideration stage, this includes purchase-related queries, putting the product in the shopping cart, etc.
This is the phase you get confident that the prospect has the potential to become a customer.
But there are cases when the transaction is postponed or cancelled even after going through all the stages of the marketing funnel.
Having a follow-up plan for such situations is essential and not giving up easily. Here are some strategies that can help you with it:
- Develop a sense Of urgency: Fear of missing out is a powerful emotion. You can use it to your advantage by creating a sense of urgency. For example, you can offer discounts that are only valid for a limited time or show that the stock is running low. This will prompt the customers to take action before it’s too late. Besides FOMO, other techniques like the scarcity principle can also be used to create a sense of urgency.
- Remarketing: Remarketing is a form of marketing that helps you reach out to people who have already shown an interest in your product or service. For example, if someone visited your website but didn’t make a purchase, or added your product to the cart and left, you can show them targeted ads the next time they’re online. This will remind them of your brand and what you offer, and it might just be enough to persuade them to purchase.
- Use Testimonials And Social Proof: Customer testimonials on checkout pages can help increase sales as it helps build trust and credibility. You can also use social validation by displaying the number of people who have already bought the product. This will show potential customers that others are using the product and are happy with it, which will encourage them to buy it as well.
- Maintain A Human Touch: If selling on an eCommerce store, you can ensure human touch by adding a live chat option.
- Make It Easy For Them: A difficult or lengthy checkout process will only discourage customers from buying your product. Make sure the process is as smooth and easy as possible, so they don’t have any trouble completing it.
The intent phase is also the best time to upsell or cross-sell related products to your potential customer. By offering them something else they might need, you can increase the order value and make more sales.
Evaluation
This is the last phase before the purchase is made. The customer has already decided they need the product, but they’re just making sure it’s the right one for them.
Very few customers churn at this stage, but it’s still important to make sure they have all the information they need to make an informed decision.
They cross-check the order to make sure they’re getting what they want, and they might look at reviews to see what other people think of the product.
What makes them churn at this stage are things like:
- Shipping costs: if they’re unexpectedly high, the customer might back out
- The return policy: if it’s too complicated or nonexistent, the customer might not want to risk it
- Competitor’s offers: if there’s a better deal elsewhere or a coupon code the customer didn’t know about, they might go for that instead
The goal at this stage is to give the customer everything they need to make a purchase with confidence. Marketers play smart by:
- Including shipping cost in the product price and making visible shipping cost free
- Offering a simple return policy
- Running their own coupons and promo codes
Purchase
The final stage is when the purchase is actually made. But that’s not the end of it – even after a purchase is complete, you can still nurture your customers and turn them into brand advocates. You can do this by:
- Sending a thank you email
- Asking for feedback
- Inviting customers to join your loyalty program
- Providing benefits for referrals
How Does Marketing Funnel Work?
From the marketer’s perspective, the entire funnel can be divided into three distinct objectives:
- Lead Generation
- Lead Nurture
- Lead Conversion
Lead Generation
Everyone belonging to the target audience is a prospect, but not every prospect is a lead. A lead is someone who has shown an interest in your product or service by providing their contact information, such as their name and email address.
The top of the funnel aims to identify those who are interested and convert them into qualified leads. Marketers use a number of methods to generate leads, which can be broadly classified into two categories:
- Inbound marketing: In inbound marketing, businesses create valuable content and make it easy for their target audience to find it. They then use this content to generate leads.
- Outbound marketing: In this type of marketing, businesses directly contact their target audience through channels such as emails, calls, or advertisements.
Lead Nurture
A lead is not ready to buy your product or service immediately after showing interest. They need to be nurtured before they are ready to make a purchase.
The middle of the funnel is where you nurture your leads and build a relationship with them. You do this by providing them with valuable content that is relevant to their needs. This can be done using a free trial of your product, an email course, or a valuable ebook.
While there is a considerable churn rate at this stage, it is still less than at the top of the funnel. This is because you have already engaged with your leads and built a relationship with them.
The goal of lead nurturing is to build trust with the leads and keep them moving through the funnel until they are ready to make a purchase.
Lead Conversion
The bottom of the funnel is where your leads become sales. This is the stage where you close the deal and make a sale.
The lead conversion rate is the percentage of leads that become sales. The average lead conversion rate depends on the industry, but it is usually between 2% and 5%. Last-minute offers, discounts, and personal guidance can help increase the lead conversion rate.
Marketing Funnel Examples
Even though the marketing funnel stages are universal, the way they are executed will be different for every business.
Here are a few examples of how businesses can execute each stage of the marketing funnel:
Marketing Funnel Of Shoes Brand
A shoes brand focusing mostly on offline retail sales can use the following marketing funnel:
- Awareness Stage: Advertising on billboards, TV commercials, and radio ads; using print media such as magazines to promote new products; sponsoring local events.
- Interest Stage: Sending comparison charts of the brand’s products in direct mailers; making the retail stores more attractive and inviting; providing more detailed product information on the brand’s website.
- Consideration Stage: Training sales staff in active listening so they can understand customer needs and then recommend the right product; using special technology within the store so customers can get more information about products before making a purchase.
- Intent: Providing coupons and discounts to increase the likelihood of a purchase; developing a special program that benefit customers who frequently purchase the brand’s products; developing special upselling and cross-selling bundles.
- Evaluation: Making sure that the sales staff is providing high-quality customer service; surveying customers to get feedback about the quality of products and services; offering after-sale services promise.
- Purchase: Creating a streamlined purchase process that is easy for customers to follow; making it easy for customers to return or exchange products if necessary.
Marketing Funnel Of SAAS Brand
The marketing funnel for a SAAS brand is a little different than for other types of businesses because the product is purchased differently. The steps are still the same, but the process happens over a longer period of time.
- Awareness: Creating blog content, infographics, and other informative resources that potential customers can use to learn about the product.
- Interest: Creating a landing page with a strong offer that will capture leads and turn them into subscribers.
- Consideration: Nurturing subscribers with helpful content that educates them about the product and its features.
- Intent: Creating a free trial or demo of the product so that potential customers can experience its value firsthand.
- Evaluation: Creating case studies and other customer success stories that potential customers can use to see how the product has helped others.
- Purchase: Creating a special offer or discount for subscribers who are ready to buy the product.
Bottom-Line?
A business cannot sustain itself without customers. The marketing funnel is the path that a potential customer takes from being aware of the business to becoming a paying customer. Without a marketing funnel, a business will have a difficult time growing.
But different businesses will have different marketing funnels based on their products, target market, and business model. There is no one-size-fits-all marketing funnel.
The best way to create a marketing funnel is to start with the end goal in mind and work backwards. What does the customer need to do in order to make a purchase? Once you know the answer to that, you can create a marketing funnel that will lead them there.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think about our article on How Marketing Funnels Work? in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.


![Go-To-Market Strategy [The Ultimate Guide] go-to-market strategy](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/go-to-market-strategy.webp)


![What Is Demand Generation? [The Ultimate Guide] What Is Demand Generation?](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/DEMAND-GENERATION.webp)
![Developing A Software Marketing Strategy [Detailed Guide] software marketing](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/software-marketing.webp)

![Conversion Rate Optimization [A Beginner's Guide] CONVERSION RATE OPTIMIZATION](https://www.feedough.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/CONVERSION-RATE-OPTIMIZATION-1.webp)