Gone are the days when getting a taxi to the office was a nightmare. We no longer need to wait on roadsides trying to spot a taxi and fervently waving at it, only to see it being hacked by another client. We don’t even remember having to be refused a ride in the dead of the night or on late evenings. All this – and much more, with the advent of online cab providers, through which a user can book a ride in a matter of a few minutes.
Uber, an emerging business giant, is one such ridesharing company that disrupted the industry in 2009. If you’ve ever wondered how Uber works, and more importantly, how it earns money, without you tipping anything extra, or with the prices usually cheaper than taxis, read on to decode Uber Business Model – a taxi aggregator.
What Is Uber?
Uber is an on-demand cab aggregator that operates on a smartphone application and lets you book a cab to get from point A to point B, pre-calculating the fare, estimating the time of arrival, and offering an option to split the cost with co-riders, all with a few taps on the app.
The company disrupted the entire cab industry in 2008 when the founders were not able to find a cab on a cold winter evening. It all started with a simple question – “What if you could request a ride from your phone?”
Today, the company is estimated to have over 100 million monthly active users worldwide, is a unicorn valued at ~$60 billion, and provides ride options from affordable bikes and scooters to Uber Air.
- UberX: The basic Uber ride.
- Uber Pool: Shared rides.
- Uber Comfort: New cars with extra legroom.
- Uber Green: Electric vehicles.
- Uber Black: Luxury cars.
- Bikes: On-demand electric bikes.
- Scooters: Electric scooters.
- UberXL: Vehicles with carrying capacity of up to 6 people.
- Uber Transit: Real-time public transport information.
- Uber WAV: Wheelchair accessible vehicles.
- Uber Lux: Luxury vehicles with top-rated drivers.
- Uber Black SUV: Luxury SUVs with top-rated drivers.
- Uber Taxi: Local taxicabs partnered with Uber.
- Uber Flash: A specialised taxi system designed for HongKong.
- Uber Auto: On-demand auto rickshaws.
- Uber Air: Flying vehicles.
Uber Business Model
Uber brought the concept of the aggregator business model to the world. This is a unique business model that involves building partnerships and let the partners work under your brand rather than building and developing the offering on your own.
In simple terms, Uber doesn’t own any cars. It aggregates or collects cab drivers, who drive their own cabs but work under the Uber brand name. While the actual service is provided by the partners, Uber makes sure that the service standards are met – the cabs reach on time, are clean, take the right route, and ensure the safety of the customer.
And since it was the pioneer, this specific business model is also called Uber for X business model.
How Does Uber Work?
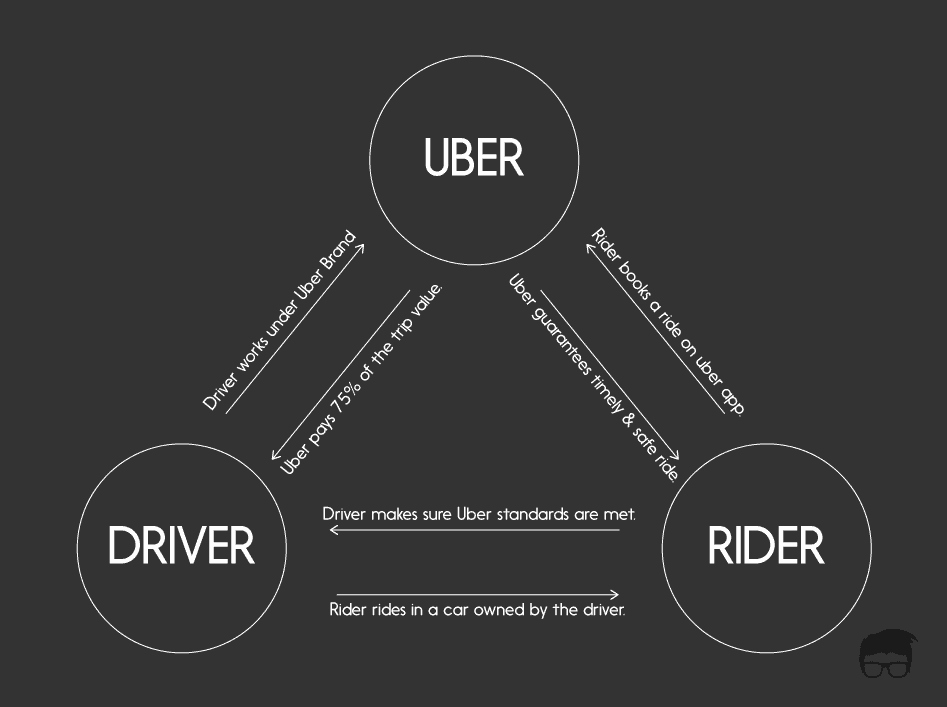
Uber works on a two faceted operating model. One aspect focuses on getting as many cab partners on board to deliver a seamless experience to the end consumer, and other aspect focuses on marketing Uber as a great ride-hailing application to the customers, that can be used to book a cab with a few taps on the smartphone.
Here’s how Uber works from the end consumer’s point of view –
The Application
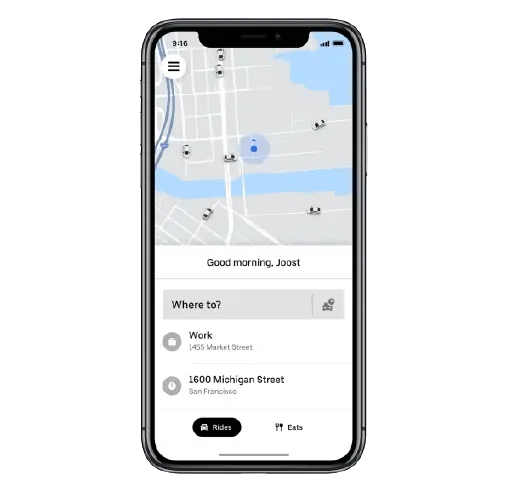
Application is the first touchpoint where the customer enters the point A and point B details. They also review and choose ride options for vehicle size, price, and estimated drop-off time; chooses the option that suits their demand; and confirm the pickup.
The Background Algorithm
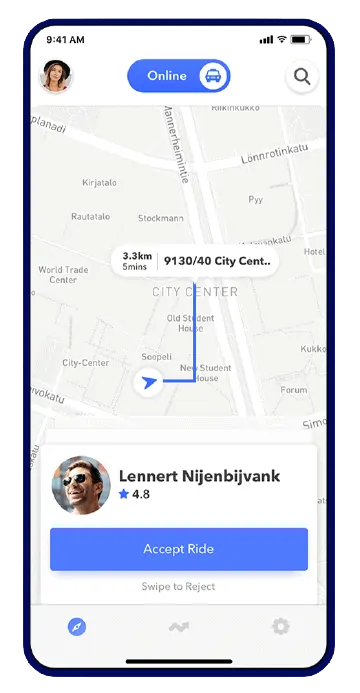
This is the backbone of the offering. The application algorithm informs all the nearby available drivers about the request who can then accept or decline the same on their own will.
However, to ensure no biasness, Uber does not show the information about the destination to the drivers before they accept the ride.
Once accepted, the rider is notified about the driver and the time it’ll take for the driver to reach the departure point.
The Cab Ride

This is where the standardisation and security aspect of the brand comes into play. Even though the cab is owned and operated by the cab driver, Uber makes sure that it carries its brand identity.
Once reached on the departure point, the rider and the driver verify each other’s names and the destination. This is often done using two-factor authentication (pin received by the rider).
The driver makes sure to follow the instructions provided by the rider.
Also, in luxurious rides, there are entertainment system and WiFi installed for the riders to use during the course of their ride. This helps in brand building.
Besides this, Uber makes sure that the rider is taking a safe ride. To do so, Uber does an in-depth background check of all the drivers that partner with the company.
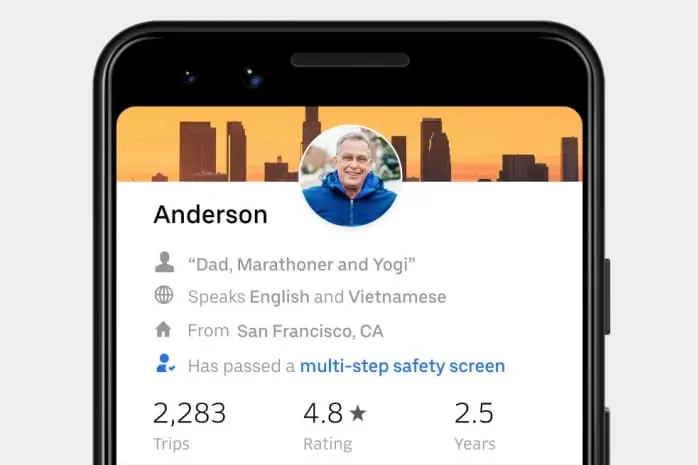
Even the riders have to verify their accounts using their phone number and/or social media accounts.
And if there’s an emergency, Uber has emergency assistance for both the riders and drivers where they can call 911 (or other emergency numbers) directly from Uber app the app displays their live location and trip details that can easily be shared with the emergency dispatcher.

Other than this, there’s also an option to share the trip details and live location with other friends and family to ensure safety.
Payment
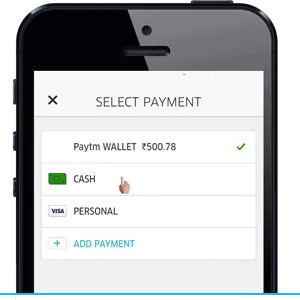
The payment policy on Uber differs for different geographies it operates in. Whatever the case may be, the payments are usually deducted after the ride is completed. It is provided in the form of cash, debit card linked to the app, credit cards, bank transfer, or wallets.
The Social Validation
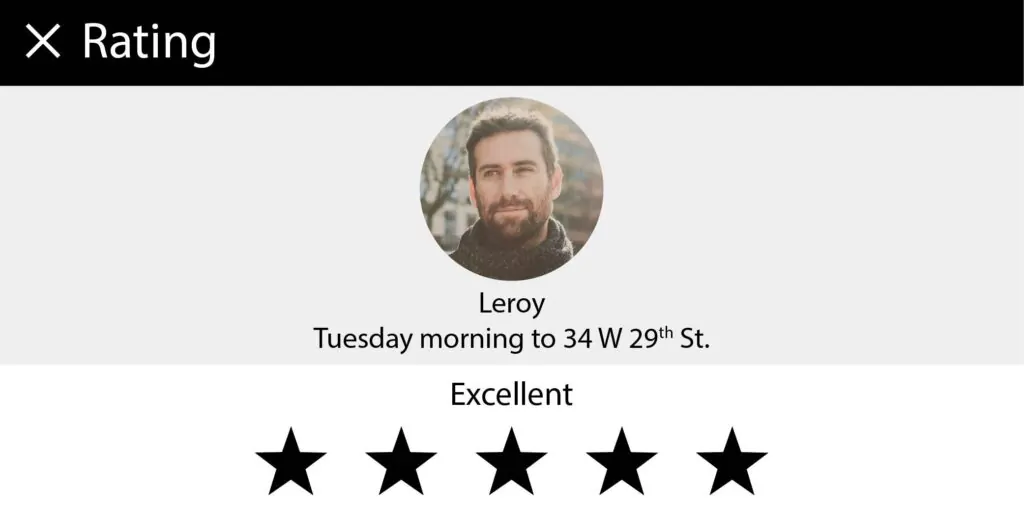
This is an operating model aspect added by Uber to make the offering more community-friendly.
After every ride, both the rider and driver get to rate each other. This rating, when aggregated with other ratings they get from other riders and drivers, is shown to the other party whenever they book or accept the ride.
Moreover, the social validation system helps the company keep a check on its drivers and make sure that they’re following the standards to keep the rider pleased. Also, a rider that doesn’t follow the terms of service is also banned, to fulfil the promise made to the drivers.
How Does Uber Make Money?
At a glance, Uber looks very similar to any other taxi company. In reality, however, it’s operating and revenue model differs from usual ride-hailing companies substantially. Since it doesn’t employ the drivers, it doesn’t own the money generated through rides.
In fact, Uber’s revenue model is a commission-based model where it charges a 20-25% fee (that differ for different geographies and class of vehicles) on all fares for the use of its brand and services by the driver.
In simple terms, Uber brings in customers to the drivers, provides their customers with payment options (like credit cards, wallets, etc.), a good application with maps, directions, ETA; and charges 20-25% of the ride fees plus other fees (like safe ride fees, booking fees, etc.) for the same.
Moreover, it’s not drivers who get to decide how much they’ll charge for the ride. Uber follows standardised prices per kilometre/mile for different classes of rides/offerings. For example, in New Delhi, a 4.5 km journey can cost from ₹21 to ₹380 depending upon the type of Uber you choose.
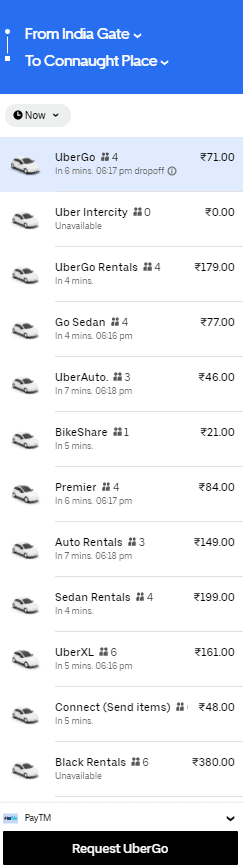
This brings us to the next section – how is this fee decided and how does uber make money through other sources than commissions?
Revenue As Commissions And other Fees
The commission of 20-25% that goes in the pocket of Uber is decided on the price paid by the customer. But how is that price calculated and what all does it include?
Well, every ride fare includes the following factors –
- Base fare: The pick up and drop price.
- Time: The amount of time spent during the ride.
- Distance: The distance the vehicle travelled during the trip (excluding the distance travelled to pick the rider up)
- Booking fee: A flat fee to help offset the administrative cost (background check, overhead, etc.). This fee goes directly into the pockets of Uber.
- Surge variable: If there’s more demand than supply, a price multiplier kicks in that increases the price.
- Tipping: A value input by the rider if he wants to tip the driver.
Dynamic Pricing Explained
During times of heavy demand (like during downpour, sporting events in the city or holidays, etc.), Uber applies dynamic pricing to its offering to ensure that riders can always receive a quick and convenient pickup.
Dynamic pricing is a technique that focuses on setting the price of the product taking into account different factors such as demand & supply, inventory, competition, locality, and other market conditions but in a smaller time frame.
It is a simple game of markup economics. With more demand, you get a lot of options to sell your limited offerings to, so you develop an algorithm that increases the price using a markup multiple that is positively correlated with the increase in demand.
For example, if the demand is doubled, your markup multiple can be 2x. That is, a ride where the rider used to pay $10 will now cost $20.
Since Uber has to fulfil the demand to maintain its brand image, dynamic pricing mechanics helps it to manage its inventory better by bringing in more drivers to the place of surge pricing in a lookout for more money per trip; all this while making more profits.
Promotional Partnerships
Uber, because of its huge user-base, is a huge attraction to bigger brands who are looking for partnerships as a part of their marketing strategies. Besides revenue as commissions from drivers, Uber business model also includes revenue generated through promotional partnerships. The company has been seen partnering with the following brands in the past – Pepsi, Hilton, BMW, Starwood, Spotify, etc. These collaborations result in a win-win situation for all the parties as-
- Customers benefit from marketing campaigns run by other brands (Uber passengers in select cities were treated to free trips in the BMW 7 Series to promote the new car),
- Uber gets the money.
- Brands get the audience.
Future Of Uber
Even though the company has a truly disruptive business model, its revenue model hasn’t proved to be profitable yet. The 2019 gross bookings totalled $65 billion, up from $50 billion in 2018. This brings in the net revenue (~25% of gross bookings) in 2019 to be $16.25 billion.
Still, Uber operates in a loss.
But seeing the trends and increasing demand for on-demand services, it’s sure that the company will be profitable in future.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of our article on Uber Business Model | How does Uber Make Money? in the comments section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.